2025-02-11 バージニア工科大学 (Virginia Tech)
<関連情報>
- https://news.vt.edu/articles/2025/02/research_fralinbiomed_memorycircuits_0207.html
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-025-85958-4
海馬CA2ニューロンにおけるMCU発現は樹状突起ミトコンドリア形態とシナプス可塑性を調節する MCU expression in hippocampal CA2 neurons modulates dendritic mitochondrial morphology and synaptic plasticity
Katy E. Pannoni,Quentin S. Fischer,Renesa Tarannum,Mikel L. Cawley,Mayd M. Alsalman,Nicole Acosta,Chisom Ezigbo,Daniela V. Gil,Logan A. Campbell & Shannon Farris
Scientific Reports Published:06 February 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-025-85958-4
Abstract
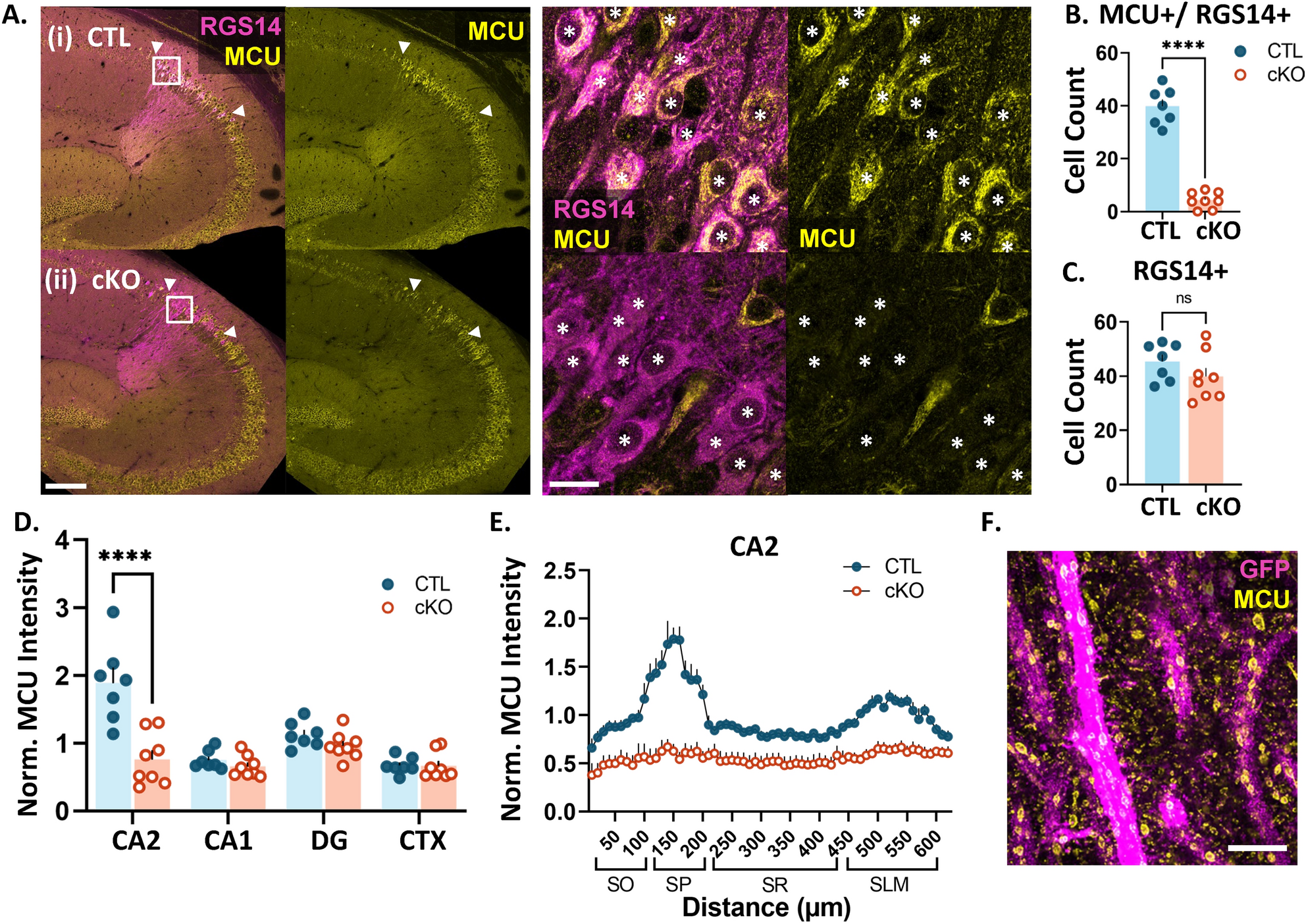
Neuronal mitochondria are diverse across cell types and subcellular compartments in order to meet unique energy demands. While mitochondria are essential for synaptic transmission and synaptic plasticity, the mechanisms regulating mitochondria to support normal synapse function are incompletely understood. The mitochondrial calcium uniporter (MCU) is proposed to couple neuronal activity to mitochondrial ATP production, which would allow neurons to rapidly adapt to changing energy demands. MCU is uniquely enriched in hippocampal CA2 distal dendrites compared to proximal dendrites, however, the functional significance of this layer-specific enrichment is not clear. Synapses onto CA2 distal dendrites readily express plasticity, unlike the plasticity-resistant synapses onto CA2 proximal dendrites, but the mechanisms underlying these different plasticity profiles are unknown. Using a CA2-specific MCU knockout (cKO) mouse, we found that MCU deletion impairs plasticity at distal dendrite synapses. However, mitochondria were more fragmented and spine head area was diminished throughout the dendritic layers of MCU cKO mice versus control mice. Fragmented mitochondria might have functional changes, such as altered ATP production, that could explain the structural and functional deficits at cKO synapses. Differences in MCU expression across cell types and circuits might be a general mechanism to tune mitochondrial function to meet distinct synaptic demands.