2025-03-13 東京大学
<関連情報>
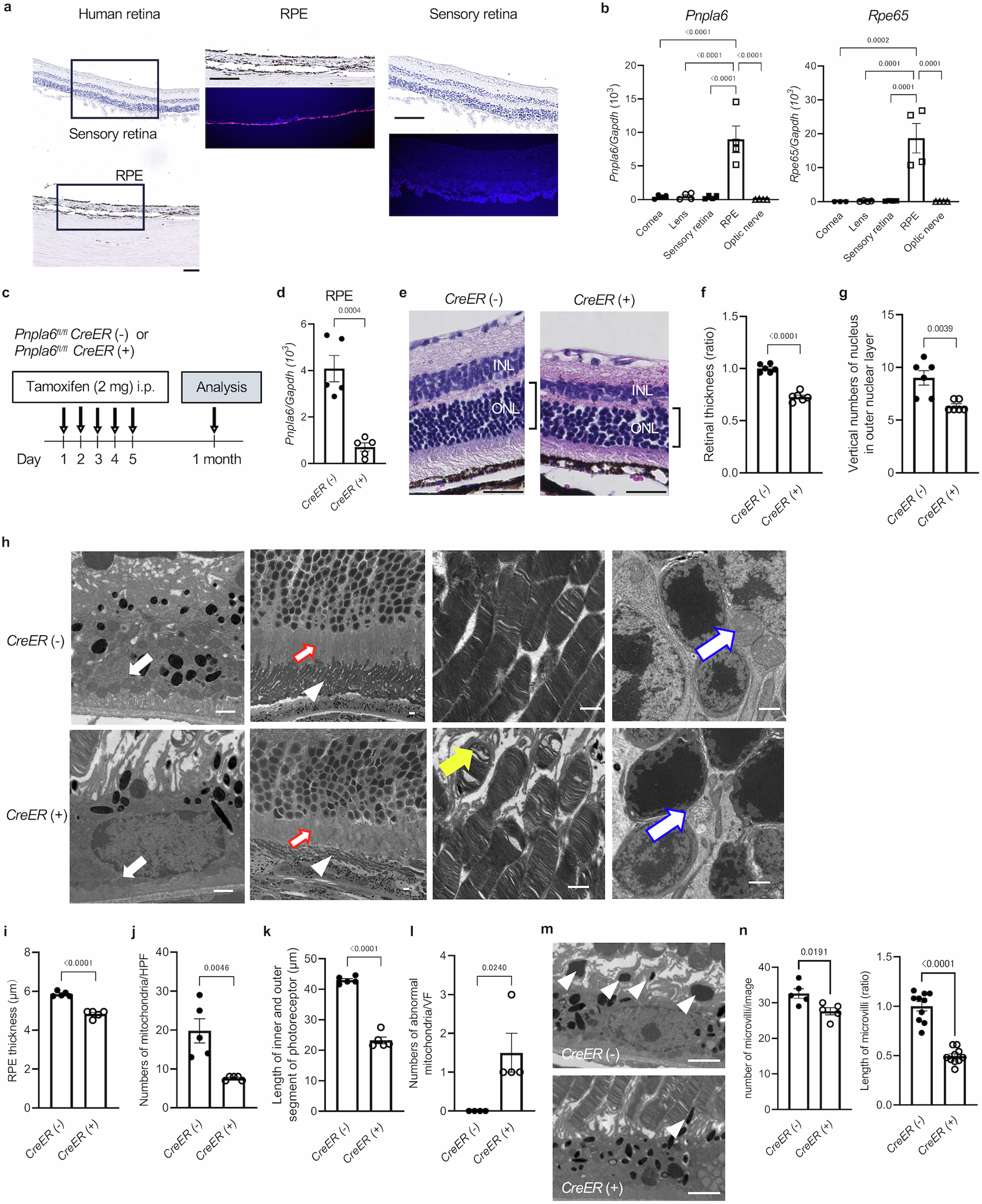
PNPLA6はリン脂質のターンオーバーを介してコリンによる網膜恒常性を制御する PNPLA6 regulates retinal homeostasis by choline through phospholipid turnover
Takashi Ono,Yoshitaka Taketomi,Takayoshi Higashi,Hiroyasu Sato,Chika Mochizuki-Ono,Yuki Nagasaki,Takashi Ueta,Takashi Miyai,Suzumi M. Tokuoka,Yoshiya Oda,Yasumasa Nishito,Tomio Ono,Choji Taya,Satoru Arata,Sumiko Watanabe,Tomoyoshi Soga,Tetsuya Hirabayashi,Makoto Aihara & Makoto Murakami
Nature Communications Published:13 March 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-025-57402-8
Abstract
Although mutations in human patatin-like phospholipase PNPLA6 are associated with hereditary retinal degenerative diseases, its mechanistic action in the retina is poorly understood. Here, we uncover the molecular mechanism by which PNPLA6 dysfunction disturbs retinal homeostasis and visual function. PNPLA6, by acting as a phospholipase B, regulates choline mobilization from phosphatidylcholine and subsequent choline turnover for phosphatidylcholine regeneration in retinal pigment epithelial cells. PNPLA6-driven choline is supplied from retinal pigment epithelial cells to adjacent photoreceptor cells to support their survival. Inhibition of this pathway results in abnormal morphology, proliferation, metabolism, and functions of retinal pigment epithelial and photoreceptor cells, and mice with retina-specific PNPLA6 deletion exhibit retinitis pigmentosa-like retinal degeneration. Notably, these abnormalities are entirely rescued by choline supplementation. Thus, PNPLA6 plays an essential role in retinal homeostasis by controlling choline availability for phospholipid recycling and provide a framework for the development of an ophthalmic drug target for retinal degeneration.


