2025-07-03 韓国基礎科学研究院 (IBS)
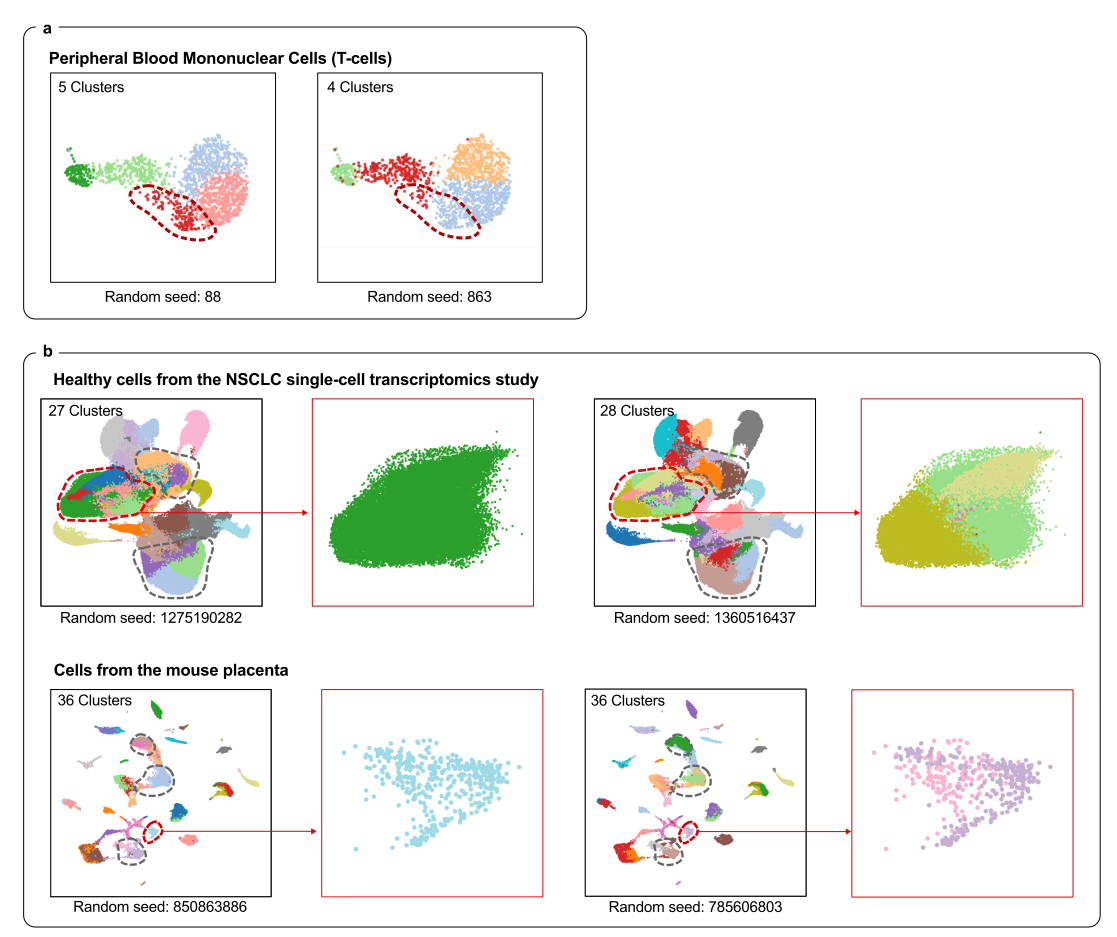 Figure 1.
Figure 1.
Cell clustering can vary wildly depending on algorithm settings like the random seed — even with the exact same data. scICE automatically detects and removes unstable groupings, giving researchers results they can trust.
<関連情報>
- https://www.ibs.re.kr/cop/bbs/BBSMSTR_000000000738/selectBoardArticle.do?nttId=25982&pageIndex=1&searchCnd=&searchWrd=#
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-025-60702-8
scICE:マルチクラスターラベル一貫性評価によるscRNA-seqデータのクラスタリングの信頼性と効率の向上 scICE: enhancing clustering reliability and efficiency of scRNA-seq data with multi-cluster label consistency evaluation
Hyun Kim,Issac Park,Jong-Eun Park,Jong Kyoung Kim,Minseok Seo & Jae Kyoung Kim
Nature Communications Published:02 July 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-025-60702-8
Abstract
Clustering analysis is a fundamental step in scRNA-seq data analysis. However, its reliability is compromised by clustering inconsistency among trials due to stochastic processes in clustering algorithms. Despite efforts to obtain reliable and consensus clustering, existing methods cannot be applied to large scRNA-seq datasets due to high computational costs. Here, we develop the single-cell Inconsistency Clustering Estimator (scICE) to evaluate clustering consistency and provide consistent clustering results, achieving up to a 30-fold improvement in speed compared to conventional consensus clustering-based methods, such as multiK and chooseR. Application of scICE to 48 real and simulated scRNA-seq datasets, some with over 10,000 cells, successfully identifies all consistent clustering results, substantially narrowing the number of clusters to explore. By enabling the focus on a narrower set of more reliable candidate clusters, users can greatly reduce computational burden while generating more robust results.

00439-8/asset/0c1c92bd-32f4-4cdc-a101-52a38bc6e8f8/main.assets/gr1_lrg.jpg)
