2025-07-30 東京大学
ChatGPT:
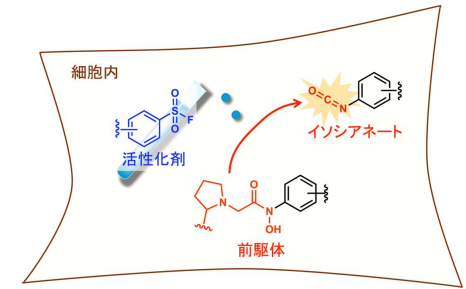
オンデマンドでのイソシアネート生成反応を用いたタンパク質修飾法
<関連情報>
- https://www.u-tokyo.ac.jp/focus/ja/press/z0111_00086.html
- https://www.u-tokyo.ac.jp/content/400268482.pdf
- https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/jacs.5c11603
オンデマンドイソシアネート形成による誘導型バイオコンジュゲーション Induced Bioconjugation via On-Demand Isocyanate Formation
Yuki Yamanashi,Menghan Xu,Shigehiro A. Kawashima,and Motomu Kanai
Journal of the American Chemical Society Published: July 26, 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.5c11603
Abstract
Selective bioconjugation reactions, exemplified by bioorthogonal chemistry, constitute a fundamental and broadly applicable tool across diverse fields, enabling precise biomolecular modifications in complex biological environments. Despite significant progress, the application of highly reactive electrophilic warheads, such as isocyanates, remains constrained by a trade-off between reactivity and selectivity, as well as hydrolytic decomposition. Here, we report a novel bioconjugation strategy that generates isocyanates on demand from a stable hydroxamic acid–pyrrolidine conjugate precursor and a sulfonyl fluoride activator. Utilizing rapid and reversible boronic ester formation, this “isocyanate surrogate” approach enables selective protein labeling with reaction rates reaching up to 104 M–1 s–1. Our findings highlight the utility of this strategy as a practical and versatile tool for inducible and selective biomolecular labeling in biological systems.