2025-08-05 国立遺伝学研究所
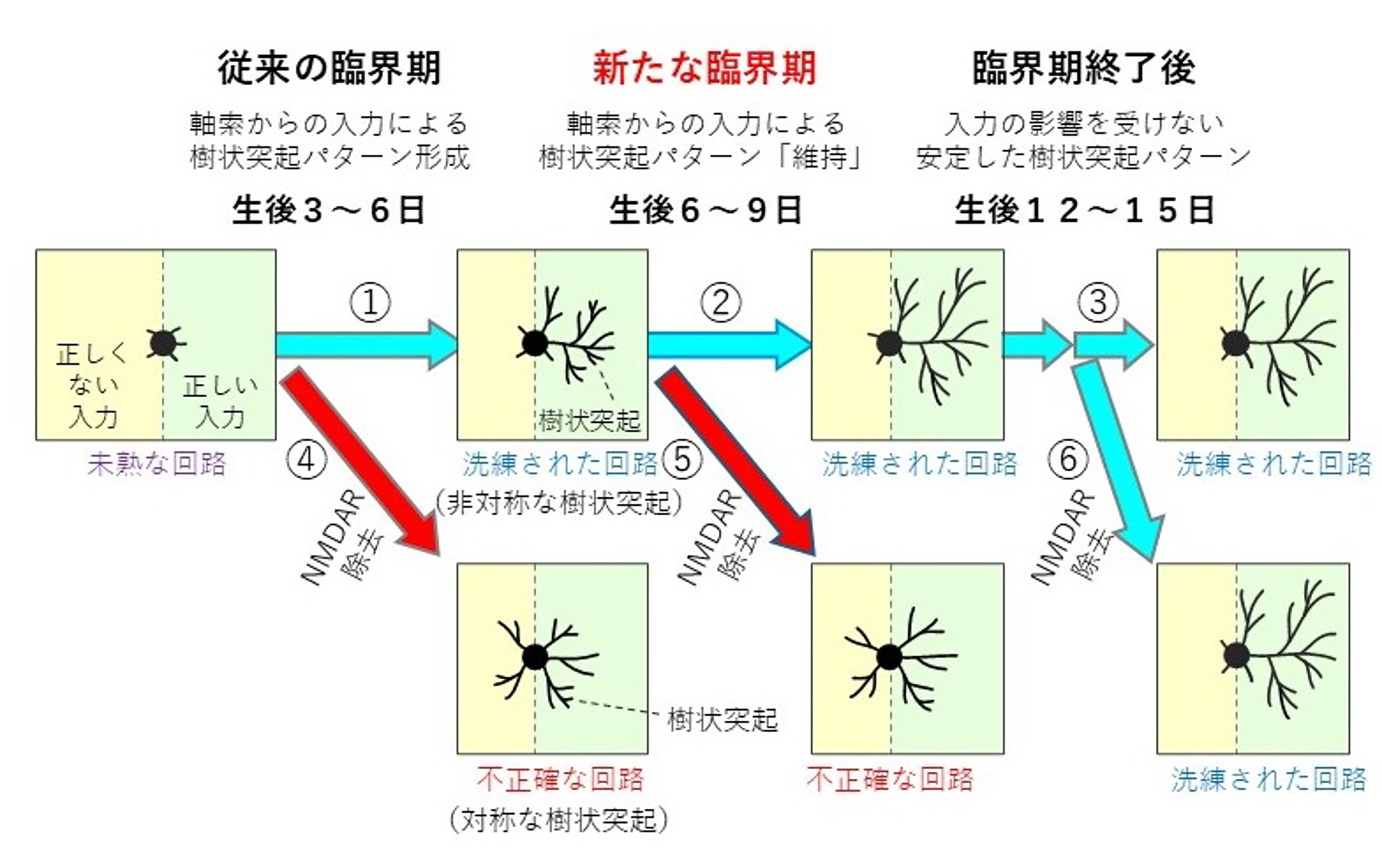 図: AID2法を用いた発達段階特異的なNMDAR除去が見出した、神経回路精緻化の「新たな臨界期」
図: AID2法を用いた発達段階特異的なNMDAR除去が見出した、神経回路精緻化の「新たな臨界期」
<関連情報>
- https://www.nig.ac.jp/nig/ja/2025/08/research-highlights_ja/pr20250729.html
- https://www.nig.ac.jp/nig/images/research_highlights/PR20250729.pdf
- https://www.cell.com/iscience/fulltext/S2589-0042(25)01490-7
誘導可能なNMDA受容体ノックダウンにより、バレル皮質神経細胞の樹状突起の精緻化における維持段階が明らかになる Inducible NMDA Receptor Knockdown Reveals a Maintenance Phase in Dendritic Refinement of Barrel Cortex Neurons
Ayane Nihashi ∙ Naoki Nakagawa, ∙ Takuya Sato ∙ … ∙ Yumiko Yoshimura, ∙ Masato T. Kanemaki ∙ Takuji Iwasato
iScience Published:July 29, 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isci.2025.113229
HIGHLIGHTS
- AID2 enabled efficient protein knockdown in postnatal mouse brain
- NMDARs were knocked down postnatally in a sparse set of cortical neurons.
- Postnatal NMDAR knockdown rapidly disrupted formed dendritic patterns
- Postnatal NMDAR knockdown eliminated Golgi lateral polarity
SUMMARY
The temporal mechanisms of activity-dependent dendritic patterning during postnatal development remain unclear because appropriate technology is lacking. Here, we demonstrate that the auxin-inducible degron 2 technology enables the rapid knockdown of target proteins at specific time points in the postnatal mouse brain. When N-methyl-D-aspartate-type glutamate receptor (NMDAR) depletion was induced from postnatal day (P)3, barrel cortex layer 4 spiny stellate neurons (barrel cells) failed to form strong asymmetry and a high tree-length variance in the dendritic patterns. Intriguingly, these unique dendritic patterns of barrel cells formed by P6 were rapidly canceled by NMDAR depletion from P6 but not from P12. NMDAR depletion from P6 also extinguished the existing Golgi apparatus’ lateral polarity. These results suggest that the barrel cells’ dendritic refinement involves not only formation but also “maintenance” of specific dendritic patterns during early postnatal development, in which NMDARs play a critical role, likely by regulating the Golgi polarity.