2025-11-13 長寿医療研究センター
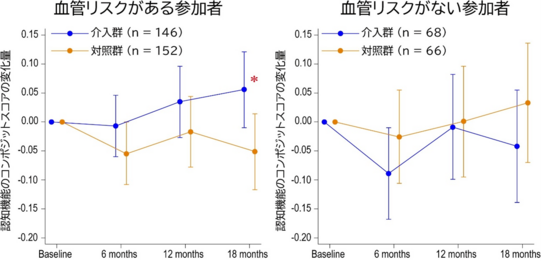
図1 血管リスクの有無による多因子介入プログラムの効果の違い
<関連情報>
- https://www.ncgg.go.jp/ri/report/20251113.html
- https://www.ncgg.go.jp/ri/report/documents/20251113.pdf
- https://alz-journals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/alz.70822
血管リスクのある高齢者に対する多領域介入の有効性:認知症予防のための日本多元的介入試験(J-MINT) Efficacy of a multidomain intervention in older adults with vascular risks: The Japan-Multimodal Intervention Trial for the Prevention of Dementia (J-MINT)
Taiki Sugimoto, Kazuaki Uchida, Yoko Yokoyama, Ayaka Onoyama, Hisashi Noma, Hidenori Arai, Takashi Sakurai, J-MINT study group
Alzheimer’s & Dementia Published: 12 November 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1002/alz.70822
Abstract
INTRODUCTION
Whether untreated or uncontrolled vascular risk factors (VRFs), such as blood pressure, glycated hemoglobin, and high-density lipoprotein (HDL) and non-HDL cholesterol levels, modify the effects of multidomain interventions on cognitive decline in mild cognitive impairment (MCI) was examined.
METHODS
Participants aged 65 to 85 years with MCI were randomized into intervention or control groups. The outcome was the change in the average Z score of the neuropsychological tests over 18 months. Interaction effects between the intervention and the presence of untreated or uncontrolled VRFs were assessed using a mixed-effects model for repeated measures.
RESULTS
Among the participants, 298 had at least one untreated or uncontrolled VRF. Significant intervention and VRF interaction (p = 0.032) indicated significant cognitive benefits in individuals with VRFs (Z score difference: 0.11; 95% confidence interval: 0.02-0.20), unlike in those without VRFs.
DISCUSSION
Individuals with untreated or uncontrolled VRFs may derive greater cognitive benefits from multidomain interventions.
CLINICAL TRIAL REGISTRATION NUMBER
This trial was registered with the UMIN-CTR (UMIN000038671).
Highlights
- We examined whether untreated or uncontrolled vascular risk factors (VRFs) modified the intervention effect.
- A significant interaction was found between the multidomain intervention and VRFs.
- The intervention was effective in individuals with untreated or uncontrolled VRFs.
- Beneficial effects on systolic blood pressure and pulse pressure were observed.
- Beneficial effects on high-density lipoprotein cholesterol and triglycerides were noted.

