2025-12-01 ゲーテ大学

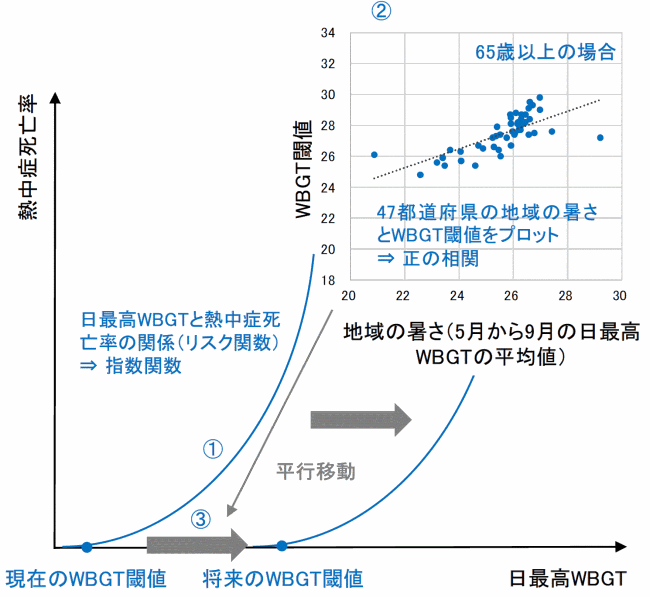
Top row: The cryo-ET averages of the gap junction channels (left) revealed striking caps (right; purple) on the inside of the cell. Bottom row: The gap junctions (light blue) allow cells to communicate across their membranes (gray) (Image: N. Rosenkranz).
<関連情報>
- https://aktuelles.uni-frankfurt.de/english/new-building-blocks-of-cell-communication-how-an-invisible-cap-could-control-electrical-synapses/
- https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/sciadv.aea8596
ギャップジャンクション-ストマチン複合体のin situ構造 In situ structure of a gap junction–stomatin complex
Nils Rosenkranz, Alexandra N. Birtasu, Konstantin Wieland, Lisa Rehm, […] , and Alexander Gottschalk
Science Advances Published:5 Nov 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.aea8596
Abstract
Gap junctions (GJs) are intercellular channels that mediate electrical signals and transfer of small molecules. They are crucial for brain, heart, and other organ functions. While molecular structures of purified homomeric GJs are available, information of in situ structures is lacking. In vivo, GJs can form heteromers with different functionalities and may associate with other proteins. Here, we analyzed Caenorhabditis elegans GJs by cryo–electron tomography and subtomogram averaging. We observed hexagonal arrays of GJs at cellular junctions in primary embryonal cells that displayed distinct wide and narrow conformations. Moreover, we found a cap-like, cytosolic protein assembly enclosing the channel pore. We propose that the cap is formed by the stomatin UNC-1, known to interact with UNC-9 innexins. This is corroborated by matching AlphaFold3 models of UNC-1 multimers with our subtomogram average structure; by expressing GFP-tagged UNC-1, leading to cap structures with additional density; and by coarse-grained MD simulations. UNC-1/stomatin rings may affect GJ formation or functions, possibly beyond nematodes.