2026-01-14 北海道大学
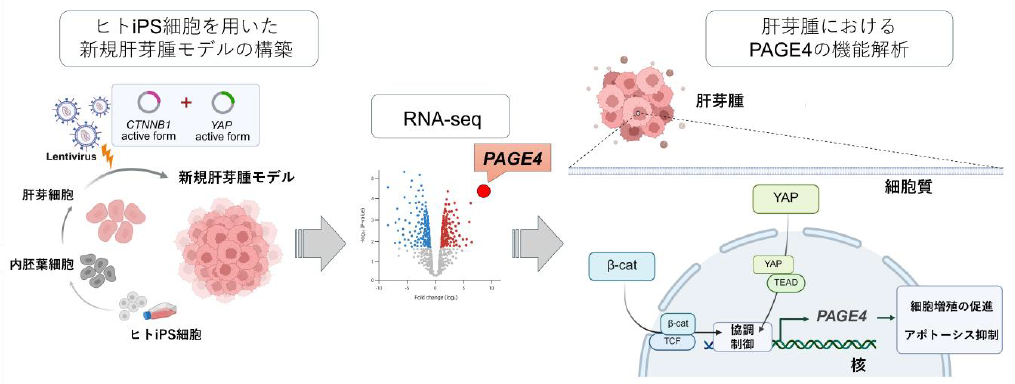
ヒトiPS細胞由来肝芽細胞にβ-catenin及びYAPを活性化することで肝芽腫様細胞を誘導し、網羅的解析により同定されたPAGE4が肝芽腫の増殖と生存を促進することを示した。
<関連情報>
- https://www.hokudai.ac.jp/news/2026/01/ipspage4.html
- https://www.hokudai.ac.jp/news/pdf/260114_pr2.pdf
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0006291X25015402
ヒトiPS細胞由来肝芽腫モデルを用いて同定されたPAGE4は肝芽腫の進展を促進する PAGE4, upregulated in a novel iPSC-derived hepatoblastoma model, promotes hepatoblastoma progression
Issei Kawakita, Shohei Honda, Yuta Yamada, Shugo Tanaka, Yuko Katayama, Takeshi Shionoiri, Asuka Ishii, Hiroyuki Kurosu, Kazuya Hamada, Kentaro Kumagai, Kensuke Nakazono, Rino Saito, Chihiro Terasaka, Ryo Takahashi, Insu Kawahara, Momoko Ara, Sari Iwasaki, Satoshi Tanaka, Atsushi Niida, Eiso Hiyama…Koji Taniguchi
Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications Available online: 16 October 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2025.152824
Highlights
- A novel hepatoblastoma model was established by introducing active CTNNB1 and YAP into iPSC-derived hepatoblasts.
- RNA-seq identified PAGE4 as a candidate gene involved in hepatoblastoma development, and its expression was further confirmed in hepatoblastoma patient samples.
- PAGE4 enhanced proliferation and survival of hepatoblastoma cell lines.
- PAGE4, a cancer/testis antigen with strictly tumor-specific expression, represents a highly attractive and clinically actionable immunotherapeutic target for hepatoblastoma.
Abstract
Hepatoblastoma is a primary malignant liver tumor in children, thought to arise from abnormal liver development during the fetal period. Approximately 90 % of cases harbor activating mutations in CTNNB1, which encodes β-catenin, while other genetic mutations are rare. Recent studies have shown that CTNNB1 mutations are frequently accompanied by increased expression of the transcriptional coactivator YAP, which promotes cell proliferation and suppresses apoptosis. Based on these findings, we established a hepatoblastoma model by introducing constitutively active forms of CTNNB1 and YAP into human induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC)-derived hepatoblasts. Cells transduced with both genes showed distinct morphological changes and upregulation of CTNNB1, YAP, and their downstream target genes. RNA-seq followed by Gene Set Enrichment Analysis (GSEA) revealed that the gene expression profile of these cells closely matches that of hepatoblastoma patients. Utilizing this model, we identified Prostate-Associated Gene 4 (PAGE4) as a novel candidate gene involved in hepatoblastoma progression. Furthermore, immunohistochemistry of hepatoblastoma specimens confirmed that PAGE4 is indeed expressed at higher levels compared to normal liver tissue. Functional analysis in hepatoblastoma cell lines demonstrated that PAGE4 plays a role in promoting cell proliferation and resistance to apoptosis. Since PAGE4 is a known cancer/testis antigen with tumor-specific expression, our findings highlight it as a novel and promising therapeutic target for hepatoblastoma, particularly in the context of cancer immunotherapy.