2026-01-28 東京大学
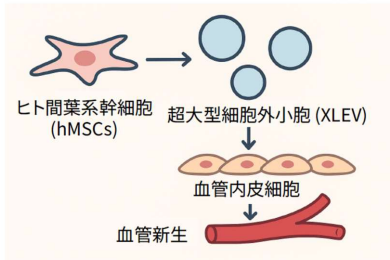
ヒト間葉系幹細胞由来 SHH 含有 XLEVs による血管新生促進の概念図
<関連情報>
- https://www.u-tokyo.ac.jp/content/400279005.pdf
- https://isevjournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/jex2.70112
血管新生ソニックヘッジホッグを含む特大細胞外小胞の非定型的な分泌はPI3K-Rab18-GDPシグナル伝達によって駆動される Unconventional Secretion of Angiogenic Sonic Hedgehog–Containing Extra-Large Extracellular Vesicles is Driven by PI3K–Rab18-GDP Signalling
Shuo Wang, Rio Imai, Yuya Kaneko, Yosuke Tanaka
Journal of Extracellular Biology Published: 28 January 2026
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1002/jex2.70112
ABSTRACT
Extra-large extracellular vesicles (XLEVs), with diameters > 600 nm, are increasingly recognised as mediators of specialized modes of intercellular communication; however, the molecular mechanisms governing their biogenesis and functional regulation remain poorly understood. Here, we show that PI3K–Rab18-GDP signalling promotes the secretion of XLEVs from human mesenchymal stem cells (hMSCs) and fibroblasts. These vesicles are highly enriched in sonic hedgehog (SHH) and display potent pro-angiogenic activity. We further demonstrate that Rab18 functions as a key regulator of this pathway specifically in its GDP-bound form, which can be enriched by the Rab inhibitor CID1067700 or by pharmacological activation of PI3K using SF1670. Rab18-GDP preferentially accumulates in the perinuclear region, where it promotes the formation of SHH-XLEV precursors from endosomal compartments. Mechanistically, PI3K–Rab18-GDP signalling recruits heat shock protein 90α (Hsp90α) and neutral sphingomyelinase 2 (nSMase2), facilitating polarized release of SHH-XLEVs from the perinuclear–plasma membrane interface, accompanied by an Hsp90α-enriched extracellular assembly. Together, these findings identify a PI3K–Rab18-GDP–dependent secretory pathway for SHH-XLEVs and provide a framework for understanding how XLEV biogenesis is coupled to SHH-associated angiogenic signalling in developmental and regenerative contexts.

