2026-01-30 九州大学
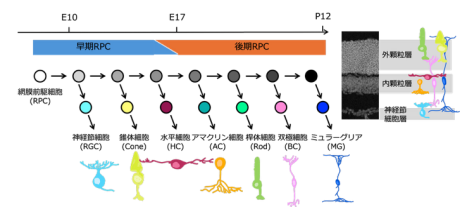
図1:網膜の発生網膜の各細胞は、共通の網膜前駆細胞 (RPC) から一定の順序で分化する(左図)。最終的に細胞体は 3 層構造となり神経回路を形成する(右図)
<関連情報>
- https://www.kyushu-u.ac.jp/ja/researches/view/1397
- https://www.kyushu-u.ac.jp/f/64499/26_0130_01.pdf
- https://www.cell.com/stem-cell-reports/fulltext/S2213-6711(25)00393-5
ヒストンメチルトランスフェラーゼSetd8は、発生中の網膜前駆細胞のアイデンティティを保護するためにクロマチンアクセシビリティを維持する Histone methyltransferase Setd8 preserves chromatin accessibility to safeguard retinal progenitor cell identity during development
Haruka Sekiryu ∙ Sakurako Shimokawa ∙ Kanae Matsuda-Ito ∙ … ∙ Koh-Hei Sonoda ∙ Kinichi Nakashima ∙ Taito Matsuda
Stem Cell Reports Published:January 29, 2026
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.stemcr.2025.102789
Highlights
•Integrated analysis reveals presistent chromatin accessibility and gene expression in RPCs
•Setd8 is expressed in embryonic retinal progenitor cells
•Setd8 deletion reduces RPC proliferation and causes sever ocular abnormalities
•Setd8 safeguards RPC identity by maintaining RPC-specific chromatin accessibility
Summary
Dynamic epigenetic changes guide retinal progenitor cells (RPCs) toward diverse neuronal subtypes and Müller glia during retinal development. However, the epigenetic mechanisms that maintain RPC proliferative and neurogenic potential throughout the final stages of retinal cell genesis remain poorly understood. Here, we integrate RNA sequencing and assay for transposase-accessible chromatin sequencing (ATAC-seq) to investigate how mouse RPC progenitor competence is regulated. Our analysis reveals conserved chromatin accessibility and gene expression profiles in mouse RPCs throughout retinal cell genesis. Notably, the histone methyltransferase Setd8, which catalyzes H4K20 monomethylation, remains persistently expressed in RPCs but is barely detectable in adult Müller glia. Setd8 deletion in developing RPCs reduces proliferation, triggers apoptosis, and disrupts retinal laminar organization and ocular axis length. Additionally, Setd8 deficiency impairs the chromatin accessibility that is normally preserved in RPCs, leading to a partial acquisition of a transcriptomic profile associated with terminally differentiated cells. Our study indicates that Setd8 safeguards mouse RPC identity by maintaining RPC-specific chromatin accessibility, thereby ensuring proper retinal development.