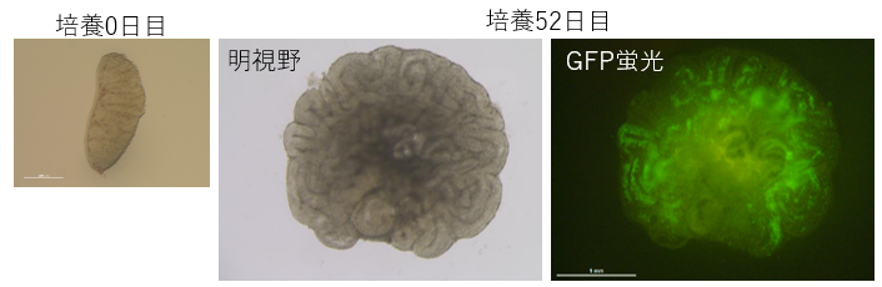
2026-02-10 東京科学大学
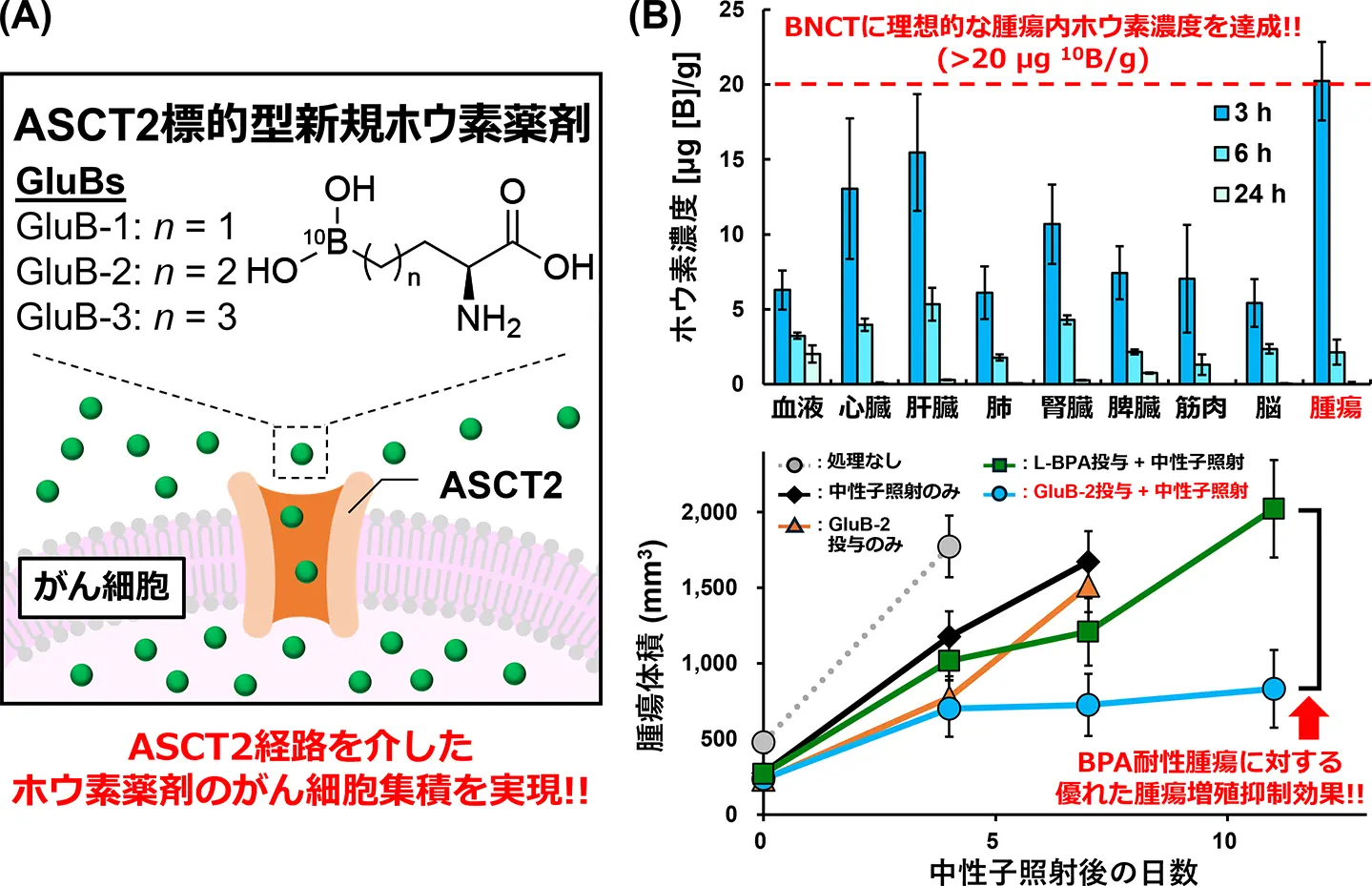
図1. (A)GluBsの分子デザインと細胞内取り込みの概要。(B)L-BPA耐性腫瘍でのGluB-2のホウ素集積と中性子捕捉療法効果
<関連情報>
- https://www.isct.ac.jp/ja/news/rcwk95t0x0rf
- https://www.isct.ac.jp/plugins/cms/component_download_file.php?type=2&pageId=&contentsId=1&contentsDataId=3171&prevId=&key=fbda2ef99d782fe25f0faefe9e537a9d.pdf
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0168365925011800
L-4-ボロノフェニルアラニン難治性腫瘍の中性子捕捉療法のためのアラニン-セリン-システイントランスポーター標的小分子ホウ素キャリア Alanine-serine-cysteine transporter-targeted small-molecule boron carriers for neutron capture therapy of L-4‑boronophenylalanine-refractory tumors
Kazuki Miura, Tomoyuki Araki, Taiki Morita, Kai Nishimura, Satoshi Okada, Minoru Suzuki, Hiroyuki Nakamura
Journal of Controlled Release Available online: 22 December 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2025.114566
Highlights
- GluBs were designed and synthesized as a new class of boron carriers targeting ASCT2.
- GluB-2 demonstrated preferential and significantly higher uptake in glioblastoma cells than BPA.
- GluB-2 demonstrated superior BNCT efficacy over BPA in a human GBM xenograft model.
Abstract
Boron neutron capture therapy (BNCT) requires the selective delivery of sufficient amounts of 10B to tumors. However, its clinical efficacy remains limited because the approved 10B agent L-4‑boronophenylalanine (BPA) relies primarily on the L-type amino acid transporter 1 (LAT1), leaving LAT1-low tumors refractory to treatment. Here, we report GluB-2, a water-soluble, alanine-serine-cysteine transporter 2 (ASCT2)-targeted small-molecule 10B carrier that expands BNCT applicability beyond BPA. GluB-2 exhibited high solubility, low cytotoxicity, and preferential ASCT2-mediated uptake in multiple cancer cell lines, particularly those with low LAT1 and high ASCT2 expression. In vivo, GluB-2 achieved tumor boron concentrations exceeding the therapeutic threshold (>20 μg [10B]/g tissue) after both intravenous and intraperitoneal administration, representing the first non-BPA small-molecule 10B carrier to reach this level. Upon thermal neutron irradiation, GluB-2 induced pronounced tumor suppression in both the CT26 allograft and the BPA-refractory U87MG xenograft models without evidence of systemic toxicity. These findings demonstrate that GluB-2 enables therapeutic small-molecule delivery of 10B to tumors through multiple dosing routes and expands the clinical applicability of BNCT beyond BPA, highlighting its translational potential.