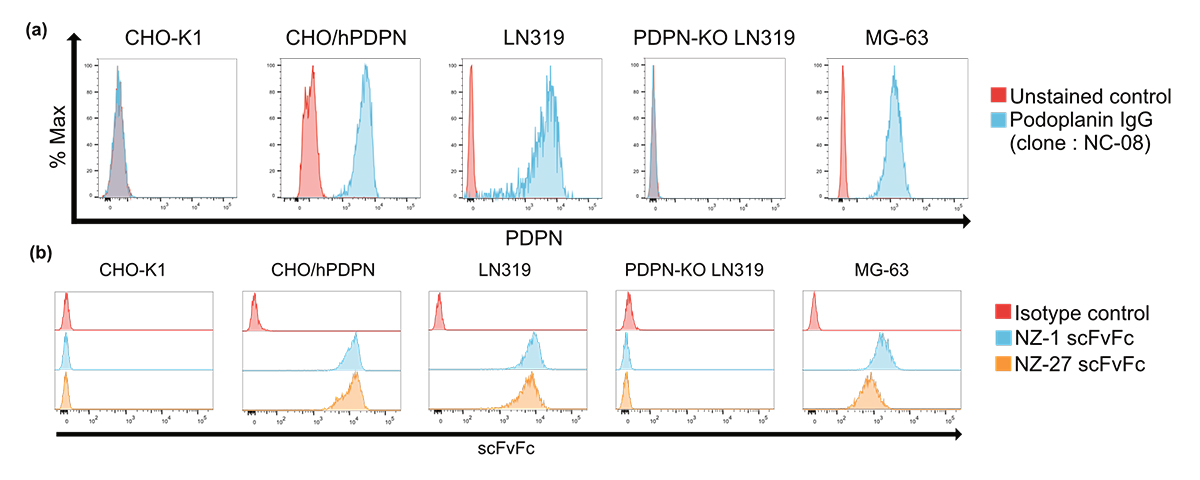
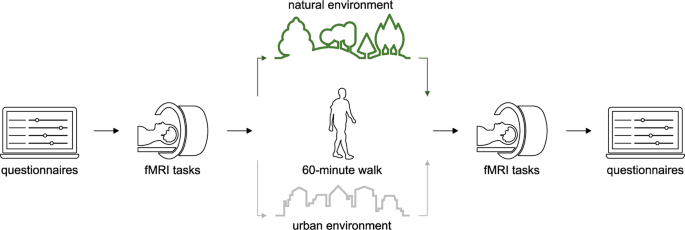
自然の中を1時間歩くと、ストレスに関連する脳の活動が低下するとの研究結果 Study shows that a one-hour walk in nature reduces stress-related brain activity
2022-09-05 マックス・プランク研究所
自然が実際に脳に影響を及ぼしたのか、それとも、特定の個人が農村部と都市部のどちらに住むかを選択したのかの因果関係を明らかにするため、リーゼ・マイトナー環境神経科学グループの研究者は、機能的磁気共鳴画像法(fMRI)を用いて、健康なボランティア63人を対象に、グルーネヴァルトの森またはベルリンの交通量の多い商店街を1時間散歩する前と後のストレス処理に関わる部位の脳活動を調査した。その結果、自然の中を歩いた後に扁桃体の活動が低下することが明らかになり、自然がストレスに関連する脳部位に有益な作用をもたらすことが示唆された。
<<関連情報>
- https://www.mpg.de/19168412/0905-bild-how-does-nature-nurture-the-brain-149835-x?c=2249
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41380-022-01720-6
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-017-12046-7
自然が育む仕組み:自然の中を1時間歩くと、扁桃体の活動が低下する。 How nature nurtures: Amygdala activity decreases as the result of a one-hour walk in nature
Sonja Sudimac,Vera Sale & Simone Kühn
Molecular Psychiatry Published:05 September 2022
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41380-022-01720-6
Abstract
Since living in cities is associated with an increased risk for mental disorders such as anxiety disorders, depression, and schizophrenia, it is essential to understand how exposure to urban and natural environments affects mental health and the brain. It has been shown that the amygdala is more activated during a stress task in urban compared to rural dwellers. However, no study so far has examined the causal effects of natural and urban environments on stress-related brain mechanisms. To address this question, we conducted an intervention study to investigate changes in stress-related brain regions as an effect of a one-hour walk in an urban (busy street) vs. natural environment (forest). Brain activation was measured in 63 healthy participants, before and after the walk, using a fearful faces task and a social stress task. Our findings reveal that amygdala activation decreases after the walk in nature, whereas it remains stable after the walk in an urban environment. These results suggest that going for a walk in nature can have salutogenic effects on stress-related brain regions, and consequently, it may act as a preventive measure against mental strain and potentially disease. Given rapidly increasing urbanization, the present results may influence urban planning to create more accessible green areas and to adapt urban environments in a way that will be beneficial for citizens’ mental health.