2023-08-23 ペンシルベニア州立大学(PennState)
◆Y染色体は性的発達に関与すると考えられてきましたが、最新の研究ではがんリスクや他の生物学的側面にも関与していることが示されています。この研究にはPenn Stateの研究者も参加し、Y染色体のアノテーションや研究への貢献を行いました。
<関連情報>
- https://www.psu.edu/news/research/story/dna-sequence-human-y-chromosome-fully-determined-first-time/
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-023-06457-y
ヒトY染色体の全塩基配列が決定 The complete sequence of a human Y chromosome
Arang Rhie,Sergey Nurk,Monika Cechova,Savannah J. Hoyt,Dylan J. Taylor,Nicolas Altemose,Paul W. Hook,Sergey Koren,Mikko Rautiainen,Ivan A. Alexandrov,Jamie Allen,Mobin Asri,Andrey V. Bzikadze,Nae-Chyun Chen,Chen-Shan Chin,Mark Diekhans,Paul Flicek,Giulio Formenti,Arkarachai Fungtammasan,Carlos Garcia Giron,Erik Garrison,Ariel Gershman,Jennifer L. Gerton,Patrick G. S. Grady,Andrea Guarracino,Leanne Haggerty,Reza Halabian,Nancy F. Hansen,Robert Harris,Gabrielle A. Hartley,William T. Harvey,Marina Haukness,Jakob Heinz,Thibaut Hourlier,Robert M. Hubley,Sarah E. Hunt,Stephen Hwang,Miten Jain,Rupesh K. Kesharwani,Alexandra P. Lewis,Heng Li,Glennis A. Logsdon,Julian K. Lucas,Wojciech Makalowski,Christopher Markovic,Fergal J. Martin,Ann M. Mc Cartney,Rajiv C. McCoy,Jennifer McDaniel,Brandy M. McNulty,Paul Medvedev,Alla Mikheenko,Katherine M. Munson,Terence D. Murphy,Hugh E. Olsen,Nathan D. Olson,Luis F. Paulin,David Porubsky,Tamara Potapova,Fedor Ryabov,Steven L. Salzberg,Michael E. G. Sauria,Fritz J. Sedlazeck,Kishwar Shafin,Valery A. Shepelev,Alaina Shumate,Jessica M. Storer,Likhitha Surapaneni,Angela M. Taravella Oill,Françoise Thibaud-Nissen,Winston Timp,Marta Tomaszkiewicz,Mitchell R. Vollger,Brian P. Walenz,Allison C. Watwood,Matthias H. Weissensteiner,Aaron M. Wenger,Melissa A. Wilson,Samantha Zarate,Yiming Zhu,Justin M. Zook,Evan E. Eichler,Rachel J. O’Neill,Michael C. Schatz,Karen H. Miga,Kateryna D. Makova & Adam M. Phillippy
Nature Published:23 August 2023
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-023-06457-y
Abstract
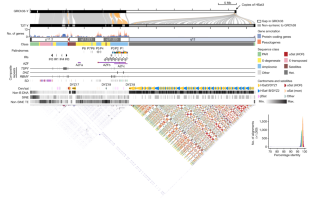
The human Y chromosome has been notoriously difficult to sequence and assemble because of its complex repeat structure that includes long palindromes, tandem repeats and segmental duplications1,2,3. As a result, more than half of the Y chromosome is missing from the GRCh38 reference sequence and it remains the last human chromosome to be finished4,5. Here, the Telomere-to-Telomere (T2T) consortium presents the complete 62,460,029-base-pair sequence of a human Y chromosome from the HG002 genome (T2T-Y) that corrects multiple errors in GRCh38-Y and adds over 30 million base pairs of sequence to the reference, showing the complete ampliconic structures of gene families TSPY, DAZ and RBMY; 41 additional protein-coding genes, mostly from the TSPY family; and an alternating pattern of human satellite 1 and 3 blocks in the heterochromatic Yq12 region. We have combined T2T-Y with a previous assembly of the CHM13 genome4 and mapped available population variation, clinical variants and functional genomics data to produce a complete and comprehensive reference sequence for all 24 human chromosomes.