2023-12-18 シンガポール国立大学(NUS)
◆研究チームはこの手法をPAINTkiller-seq assayとして発展させ、遺伝子発現の分析を含む総合的な解析を実施しました。これにより、免疫応答の複雑なメカニズムを理解し、研究および臨床応用のための重要なツールとなる可能性が示唆されています。
<関連情報>
- https://news.nus.edu.sg/nus-researchers-develop-an-innovative-and-flexible-method-to-study-immune-cell-capabilities/
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41551-023-01089-z
蛍光標的細胞溶解液の捕獲による機能的キラー細胞の同定、選別、プロファイリング Identification, sorting and profiling of functional killer cells via the capture of fluorescent target-cell lysate
Yen Hoon Luah,Tongjin Wu & Lih Feng Cheow
Nature Biomedical Engineering Published31 August 2023
DOIhttps://doi.org/10.1038/s41551-023-01089-z
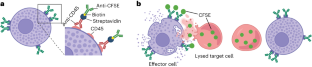
Abstract
Assays for assessing cell-mediated cytotoxicity are largely target-cell-centric and cannot identify and isolate subpopulations of cytotoxic effector cells. Here we describe an assay compatible with flow cytometry for the accurate identification and sorting of functional killer-cell subpopulations in co-cultures. The assay, which we named PAINTKiller (for ‘proximity affinity intracellular transfer identification of killer cells’), relies on the detection of an intracellular fluorescent protein ‘painted’ by a lysed cell on the surface of the lysing cytotoxic cell (specifically, on cell lysis the intracellular fluorescein derivative carboxyfluorescein succinimidyl ester is captured on the surface of the natural killer cell by an antibody for anti-fluorescein isothiocyanate linked to an antibody for the pan-leucocyte surface receptor CD45). The assay can be integrated with single-cell RNA sequencing for the analysis of molecular pathways associated with cell cytotoxicity and may be used to uncover correlates of functional immune responses.