2024-03-15 カリフォルニア大学サンタバーバラ校(UCSB)
<関連情報>
- https://news.ucsb.edu/2024/021394/reference-genomes-worlds-largest-and-smallest-mammals-pave-way-toward-solving-mysteries
- https://academic.oup.com/mbe/article/41/3/msae036/7611405
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41597-024-03011-x
シロナガスクジラの高品質ゲノム、断片的重複、歴史的人口統計学 A High-Quality Blue Whale Genome, Segmental Duplications, and Historical Demography
Yury V Bukhman, Phillip A Morin, Susanne Meyer, Li-Fang Chu, Jeff K Jacobsen, Jessica Antosiewicz-Bourget, Daniel Mamott, Maylie Gonzales, Cara Argus, Jennifer Bolin …
Molecular Biology and Evolution Published:20 February 2024
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msae036

Abstract
The blue whale, Balaenoptera musculus, is the largest animal known to have ever existed, making it an important case study in longevity and resistance to cancer. To further this and other blue whale-related research, we report a reference-quality, long-read-based genome assembly of this fascinating species. We assembled the genome from PacBio long reads and utilized Illumina/10×, optical maps, and Hi-C data for scaffolding, polishing, and manual curation. We also provided long read RNA-seq data to facilitate the annotation of the assembly by NCBI and Ensembl. Additionally, we annotated both haplotypes using TOGA and measured the genome size by flow cytometry. We then compared the blue whale genome with other cetaceans and artiodactyls, including vaquita (Phocoena sinus), the world’s smallest cetacean, to investigate blue whale’s unique biological traits. We found a dramatic amplification of several genes in the blue whale genome resulting from a recent burst in segmental duplications, though the possible connection between this amplification and giant body size requires further study. We also discovered sites in the insulin-like growth factor-1 gene correlated with body size in cetaceans. Finally, using our assembly to examine the heterozygosity and historical demography of Pacific and Atlantic blue whale populations, we found that the genomes of both populations are highly heterozygous and that their genetic isolation dates to the last interglacial period. Taken together, these results indicate how a high-quality, annotated blue whale genome will serve as an important resource for biology, evolution, and conservation research.
エトルリアトガリネズミSuncus etruscusの染色体レベルのゲノムアセンブリ Chromosome level genome assembly of the Etruscan shrew Suncus etruscus
Yury V. Bukhman,Susanne Meyer,Li-Fang Chu,Linelle Abueg,Jessica Antosiewicz-Bourget,Jennifer Balacco,Michael Brecht,Erica Dinatale,Olivier Fedrigo,Giulio Formenti,Arkarachai Fungtammasan,Swagarika Jaharlal Giri,Michael Hiller,Kerstin Howe,Daisuke Kihara,Daniel Mamott,Jacquelyn Mountcastle,Sarah Pelan,Keon Rabbani,Ying Sims,Alan Tracey,Jonathan M. D. Wood,Erich D. Jarvis,James A. Thomson,… Ron Stewart
Scientific Data Published:07 February 2024
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41597-024-03011-x
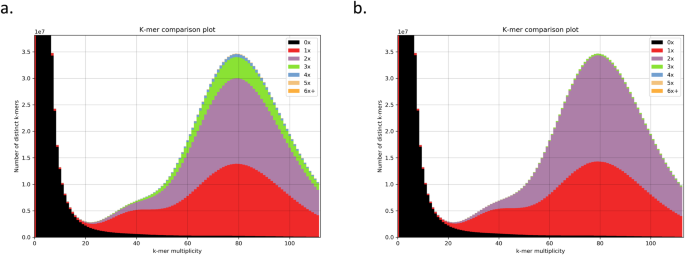
Abstract
Suncus etruscus is one of the world’s smallest mammals, with an average body mass of about 2 grams. The Etruscan shrew’s small body is accompanied by a very high energy demand and numerous metabolic adaptations. Here we report a chromosome-level genome assembly using PacBio long read sequencing, 10X Genomics linked short reads, optical mapping, and Hi-C linked reads. The assembly is partially phased, with the 2.472 Gbp primary pseudohaplotype and 1.515 Gbp alternate. We manually curated the primary assembly and identified 22 chromosomes, including X and Y sex chromosomes. The NCBI genome annotation pipeline identified 39,091 genes, 19,819 of them protein-coding. We also identified segmental duplications, inferred GO term annotations, and computed orthologs of human and mouse genes. This reference-quality genome will be an important resource for research on mammalian development, metabolism, and body size control.


