2024-07-02 ヒューストン大学(UH)
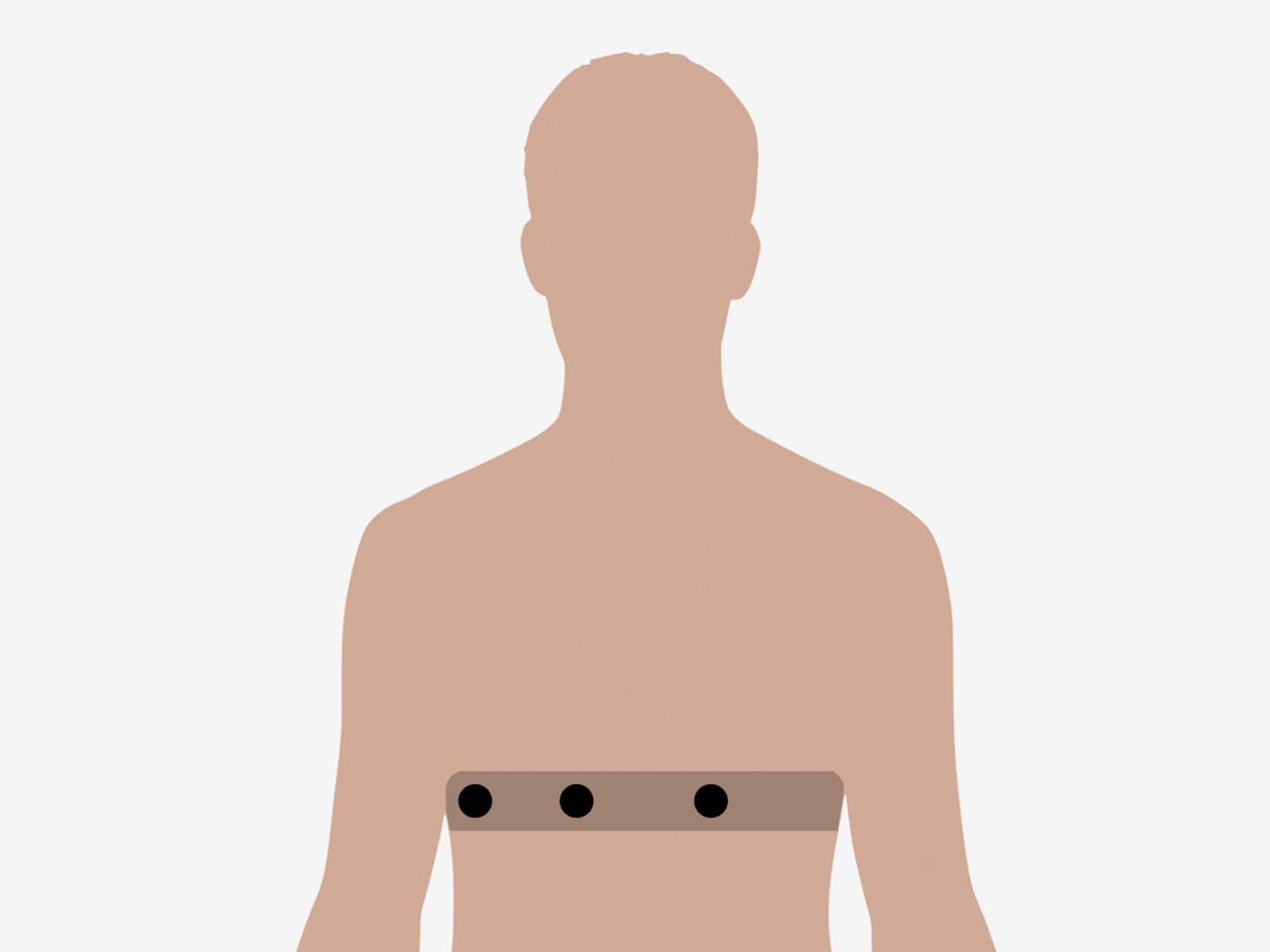
Mockup of future sleep study devices developed at University of Houston.
<関連情報>
- https://uh.edu/news-events/stories/2024/july/07022024-sheth-sleep-staging-monitoring.php
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0010482524006292?via%3Dihub
心電図のみのフィードフォワード・ニューラルネットワークを用いた専門家レベルの睡眠ステージング Expert-level sleep staging using an electrocardiography-only feed-forward neural network
Adam M. Jones, Laurent Itti, Bhavin R. Sheth
Computers in Biology and Medicine Available online: 29 April 2024
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compbiomed.2024.108545
Highlights
- Advances sleep medicine through cardiosomnography: low-cost, ECG-based sleep studies.
- Single-lead ECG-only neural network matches PSG in sleep stage scoring performance.
- Real-time scoring option enables novel interventions outside the laboratory.
- New loss function aligns the optimization goal with evaluation metric, Cohen’s kappa.
- New, extensive meta-analysis of inter-rater agreement of expert human PSG scoring.
Abstract
Reliable classification of sleep stages is crucial in sleep medicine and neuroscience research for providing valuable insights, diagnoses, and understanding of brain states. The current gold standard method for sleep stage classification is polysomnography (PSG). Unfortunately, PSG is an expensive and cumbersome process involving numerous electrodes, often conducted in an unfamiliar clinic and annotated by a professional. Although commercial devices like smartwatches track sleep, their performance is well below PSG. To address these disadvantages, we present a feed-forward neural network that achieves gold-standard levels of agreement using only a single lead of electrocardiography (ECG) data. Specifically, the median five-stage Cohen’s kappa is 0.725 on a large, diverse dataset of 5 to 90-year-old subjects. Comparisons with a comprehensive meta-analysis of between-human inter-rater agreement confirm the non-inferior performance of our model. Finally, we developed a novel loss function to align the training objective with Cohen’s kappa. Our method offers an inexpensive, automated, and convenient alternative for sleep stage classification—further enhanced by a real-time scoring option. Cardiosomnography, or a sleep study conducted with ECG only, could take expert-level sleep studies outside the confines of clinics and laboratories and into realistic settings. This advancement democratizes access to high-quality sleep studies, considerably enhancing the field of sleep medicine and neuroscience. It makes less-expensive, higher-quality studies accessible to a broader community, enabling improved sleep research and more personalized, accessible sleep-related healthcare interventions.