2025-04-02 カロリンスカ研究所(KI)
<関連情報>
- https://news.ki.se/blood-test-may-rule-out-future-dementia-risk
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41591-025-03605-x
アルツハイマー病と認知症発症の血中バイオマーカーに関する研究 Blood-based biomarkers of Alzheimer’s disease and incident dementia in the community
Giulia Grande,Martina Valletta,Debora Rizzuto,Xin Xia,Chengxuan Qiu,Nicola Orsini,Matilda Dale,Sarah Andersson,Claudia Fredolini,Bengt Winblad,Erika J. Laukka,Laura Fratiglioni &Davide L. Vetrano
Nature Medicine Published:26 March 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-025-03605-x
Abstract
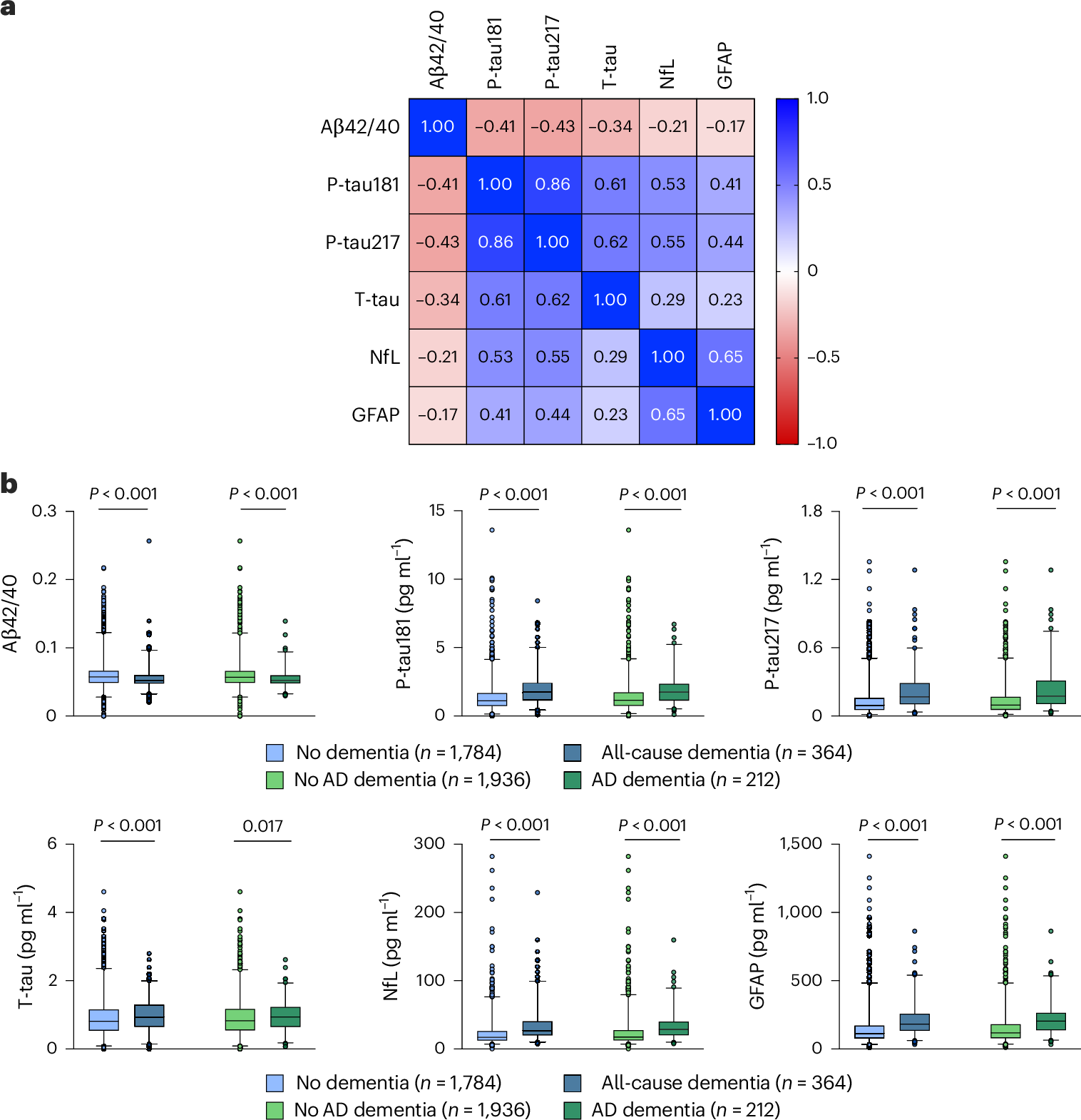
Evidence regarding the clinical validity of blood biomarkers of Alzheimer’s disease (AD) in the general population is limited. We estimated the hazard and predictive performance of six AD blood biomarkers for incident all-cause and AD dementia—the ratio of amyloid-β 42 to amyloid-β 40 and levels of tau phosphorylated at T217 (p-tau217), tau phosphorylated at T181 (p-tau181), total tau, neurofilament light chain (NfL), and glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP)—in a cohort of 2,148 dementia-free older adults from Sweden, who were followed for up to 16 years. In multi-adjusted Cox regression models, elevated baseline levels of p-tau181, p-tau217, NfL, and GFAP were associated with a significantly increased hazard for all-cause and AD dementia, displaying a non-linear dose–response relationship. Elevated concentrations of p-tau181, p-tau217, NfL, and GFAP demonstrated strong predictive performance (area under the curve ranging from 70.9% to 82.6%) for 10-year all-cause and AD dementia, with negative predictive values exceeding 90% but low positive predictive values (PPVs). Combining p-tau217 with NfL or GFAP further improved prediction, with PPVs reaching 43%. Our findings suggest that these biomarkers have the potential to rule out impending dementia in community settings, but they might need to be combined with other biological or clinical markers to be used as screening tools.