2025-05-26 神戸大学,奈良女子大学,東京大学,大阪大学
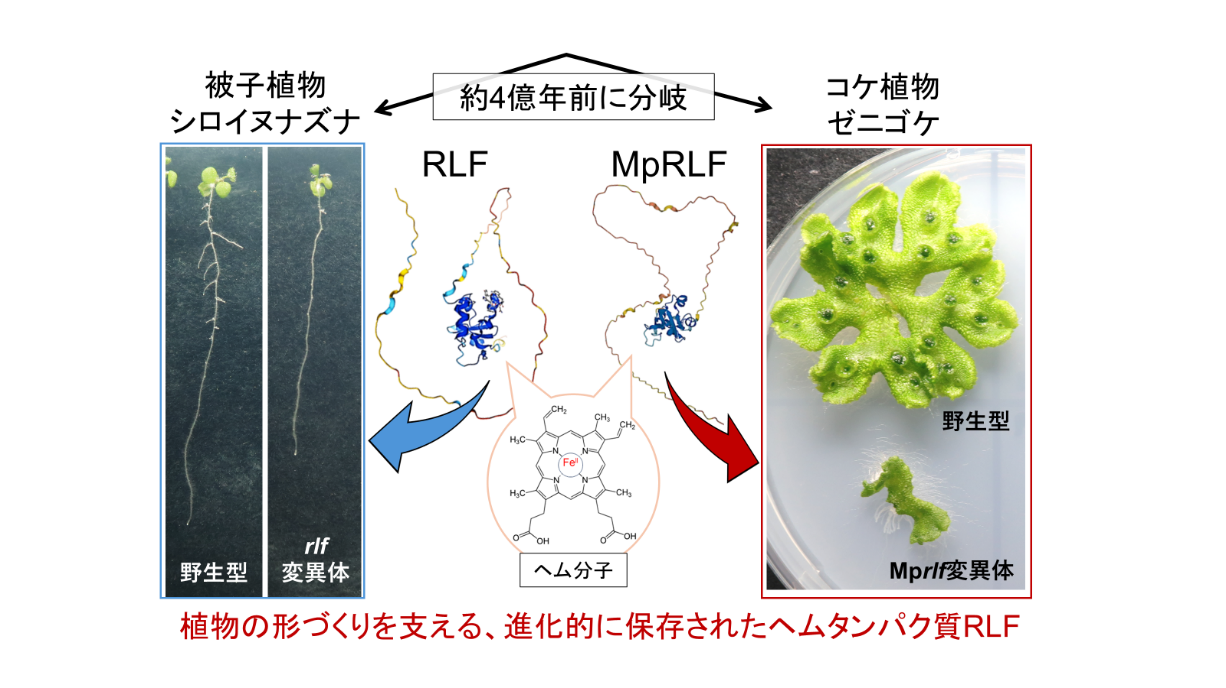
東京大学総合文化研究科の増田建教授らは、神戸大学、奈良女子大学、大阪大学と共に、植物の器官形成に関与するヘムタンパク質「RLF」が進化的に保存された重要因子であることを解明した。モデル植物シロイヌナズナとゼニゴケの両方で、RLFの欠損が器官形成異常を引き起こすことを確認。また、RLFがヘムと結合する性質を持つことから、代謝と発生を結びつける役割が示唆された。これは植物の形づくりの共通原理や進化過程の理解に貢献し、植物育種への応用も期待される。
<関連情報>
- https://www.c.u-tokyo.ac.jp/info/news/topics/20250526000100.html
- https://nph.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/nph.70181
進化的に保存されたシトクロムb5様ヘム結合タンパク質RLFがMarchantia polymorphaの器官形成を制御する Evolutionary-conserved RLF, a cytochrome b5-like heme-binding protein, regulates organ development in Marchantia polymorpha
Kentaro P. Iwata, Takayuki Shimizu, Yuuki Sakai, Tomoyuki Furuya, Hinatamaru Fukumura, Yuki Kondo, Tatsuru Masuda, Kimitsune Ishizaki, Hidehiro Fukaki
New Phytologist Published: 25 May 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.70181
Summary
- In Arabidopsis thaliana, REDUCED LATERAL ROOT FORMATION (RLF), a cytochrome b5-like heme-binding domain (Cytb5-HBD) protein, is necessary for proper lateral root (LR) formation. Whereas the other Cytb5-HBD proteins in A. thaliana regulate different metabolic reactions, RLF is unique as it specifically regulates organ development. However, it remains unknown whether heme binding to RLF is necessary for its function and whether RLF orthologs in different plant species also regulate organ development.
- We demonstrate that RLF binds to heme in vitro and that two histidine residues, which are conserved among Cytb5-HBD, are crucial for both heme binding and its biological function in A. thaliana. In addition, we show that MpRLF, a RLF ortholog in the bryophyte Marchantia polymorpha, also binds to heme in vitro and that MpRLF rescues the LR formation phenotype of the A. thaliana rlf mutant.
- Mprlfge, the loss-of-function mutation in MpRLF, resulted in delayed thallus growth and inhibited both gemma cup and reproductive organ formation.
- Our findings indicate that MpRLF is essential for proper vegetative and reproductive development in M. polymorpha. This suggests that RLF-dependent redox reaction systems are conserved across diverse plant species and were independently co-opted for organ development in bryophyte and seed plant evolution.