2025-06-12 中国科学院(CAS)
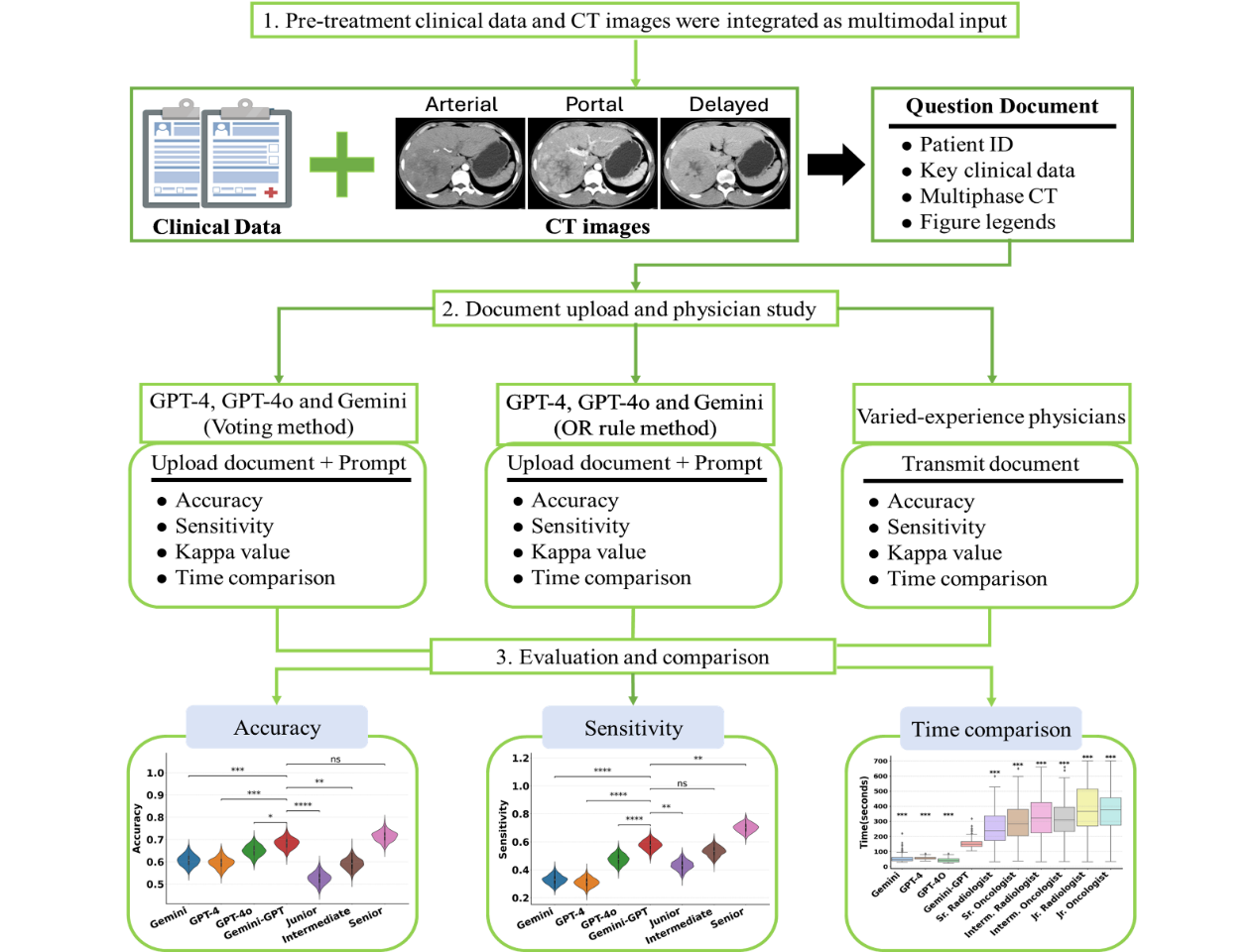
Comparative study process of LLMs and doctors in predicting immune therapy response for liver cancer (Image by WANG Tengfei)
<関連情報>
- https://english.cas.cn/newsroom/research_news/life/202506/t20250613_1045559.shtml
- https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s10916-025-02192-1
切除不能肝細胞癌における免疫療法の奏効予測:大規模言語モデルとヒト専門家の比較研究 Predicting Immunotherapy Response in Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Comparative Study of Large Language Models and Human Experts
Jun Xu,Junjie Wang,Junjun Li,Zhangxiang Zhu,Xiao Fu,Wei Cai,Ruipeng Song,Tengfei Wang & Hai Li
Journal of Medical Systems Published:15 May 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-025-02192-1
Abstract
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is an aggressive cancer with limited biomarkers for predicting immunotherapy response. Recent advancements in large language models (LLMs) like GPT-4, GPT-4o, and Gemini offer the potential for enhancing clinical decision-making through multimodal data analysis. However, their effectiveness in predicting immunotherapy response, especially compared to human experts, remains unclear. This study assessed the performance of GPT-4, GPT-4o, and Gemini in predicting immunotherapy response in unresectable HCC, compared to radiologists and oncologists of varying expertise. A retrospective analysis of 186 patients with unresectable HCC utilized multimodal data (clinical and CT images). LLMs were evaluated with zero-shot prompting and two strategies: the ‘voting method’ and the ‘OR rule method’ for improved sensitivity. Performance metrics included accuracy, sensitivity, area under the curve (AUC), and agreement across LLMs and physicians.GPT-4o, using the ‘OR rule method,’ achieved 65% accuracy and 47% sensitivity, comparable to intermediate physicians but lower than senior physicians (accuracy: 72%, p = 0.045; sensitivity: 70%, p < 0.0001). Gemini-GPT, combining GPT-4, GPT-4o, and Gemini, achieved an AUC of 0.69, similar to senior physicians (AUC: 0.72, p = 0.35), with 68% accuracy, outperforming junior and intermediate physicians while remaining comparable to senior physicians (p = 0.78). However, its sensitivity (58%) was lower than senior physicians (p = 0.0097). LLMs demonstrated higher inter-model agreement (κ = 0.59–0.70) than inter-physician agreement, especially among junior physicians (κ = 0.15). This study highlights the potential of LLMs, particularly Gemini-GPT, as valuable tools in predicting immunotherapy response for HCC.