2025-07-22 東京慈恵会医科大学,国立がん研究センター,埼玉県立循環器・呼吸器病センター
<関連情報>
- https://www.ncc.go.jp/jp/information/researchtopics/2025/0722/index.html
- https://www.ncc.go.jp/jp/information/researchtopics/2025/0722/20250722.pdf
- https://publications.ersnet.org/content/erj/early/2025/07/03/1399300300022-2025
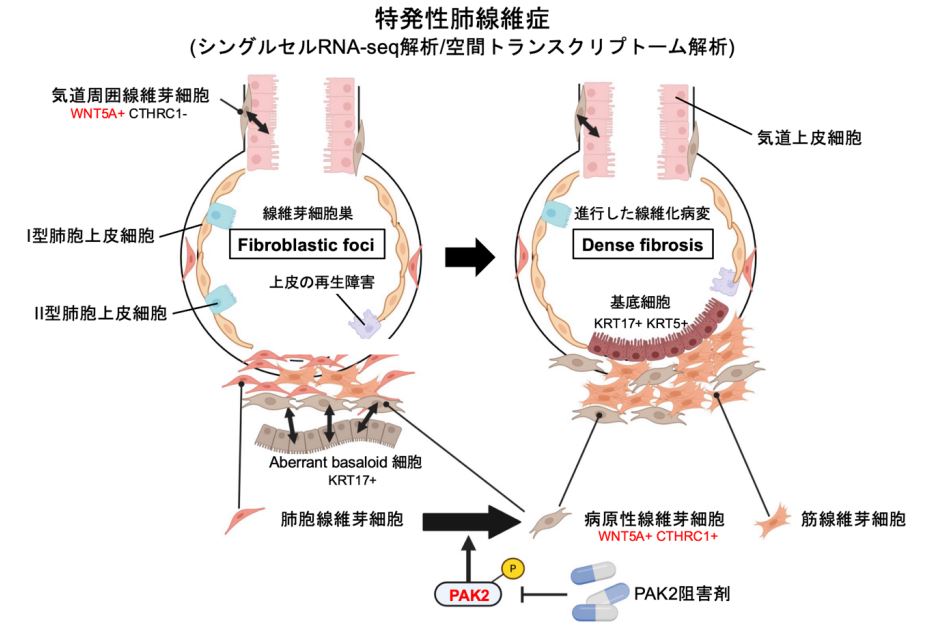
IPFの線維芽細胞病巣と高密度線維症における治療標的としてのPAKキナーゼが、統合された空間トランスクリプトミクスと単一細胞トランスクリプトミクスによって明らかになった Integrated spatial and single-cell transcriptomics reveal PAK kinase as a therapeutic target in fibroblastic foci and dense fibrosis of IPF
Naoaki Watanabe,Masahiro Yoshida ,Yuta Hirano,…
European Respiratory Journal Published:17 July 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1183/13993003.00022-2025
Abstract
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is a fatal interstitial lung disease characterized by progressive fibrosis of lung parenchyma. The histopathology of IPF exhibits temporal and spatial heterogeneity, including immature fibroblastic foci (FF) and densely collagenized fibrosis. FF serve as dynamic niches of profibrotic fibroblasts and play a pivotal role in fibrosis progression and transition into dense fibrosis (DF). Here, we integrated single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) with spatial transcriptomics to elucidate cellular heterogeneity and the novel cell type involved not only in FF formation but also in DF development. We identified a novel myofibroblast population, WNT5A+ CTHRC1+ myofibroblasts, enriched in both FF and DF regions, underscoring their pivotal role in fibrosis progression. Differential gene expression analysis revealed the activation of p21-activated kinase 2 (PAK2) in these fibrotic areas, including WNT5A+ CTHRC1+ myofibroblasts. PAK inhibition significantly suppressed TGF-β-induced myofibroblast differentiation and collagen production in IPF-derived fibroblasts. Furthermore, in a bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis mouse model, intraperitoneal administration of the PAK inhibitor significantly attenuated fibrotic progression. This study highlights the therapeutic potential of PAK inhibition for IPF, particularly targeting pathogenic fibroblasts within both FF and DF regions. By leveraging spatial transcriptomics and scRNA-seq, we provide a comprehensive molecular and cellular atlas of FF and DF in IPF lung tissue, offering new insights into fibrosis progression and therapeutic intervention.