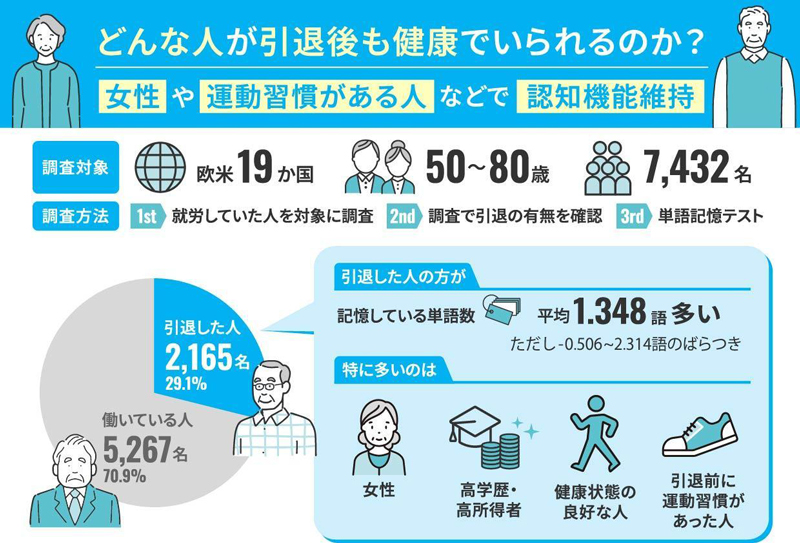
2025-12-10 国立精神・神経医療研究センター
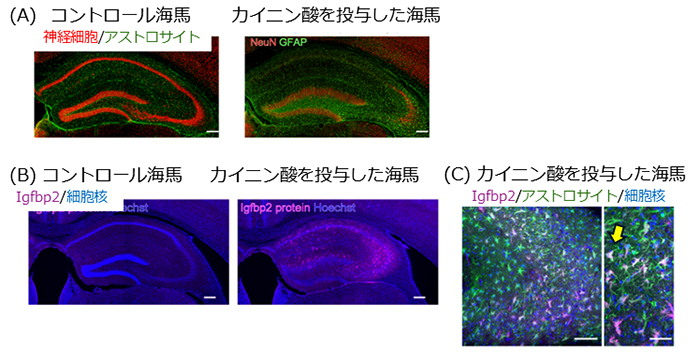
図1:MTLEモデルマウス海馬におけるIgfbp2発現
(A) カイニン酸を投与したマウスの海馬では、**神経細胞が死んで萎縮し、アストロサイトが活性化して集まる(反応性アストログリオーシス)**といった、MTLEに特徴的な構造変化が見られる。(Scale bar = 200 µm)
(B) Igfbp2 の量を比較すると、カイニン酸を投与した海馬では Igfbp2が大幅に増えていることが確認できる。
(Scale bar = 200 µm)
(C) Igfbp2 は アストロサイトと同じ場所に存在しており(共局在)、アストロサイトがIgfbp2を産生していることを示している。(Scale bar = 50 µm)
<関連情報>
- https://www.ncnp.go.jp/topics/detail.php?@uid=di6nP1mDrwxAij05
- https://www.ncnp.go.jp/press_search/images/files/PressRelease/20251210_PR.pdf
- https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/glia.70099
アストロサイトのIgfbp2は内側側頭葉てんかんのマウスモデルにおいて自発発作を促進する Astrocytic Igfbp2 Promotes Spontaneous Seizures in a Mouse Model of Mesial Temporal Lobe Epilepsy
Shinichi Kinoshita, Nobuyoshi Matsumoto, Shota Morikawa, Yuji Ikegaya, Ryuta Koyama
Glia Published: 15 November 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1002/glia.70099
ABSTRACT
Mesial temporal lobe epilepsy (MTLE) is a common, frequently drug-resistant epilepsy characterized by seizures arising from the hippocampus. Its hallmark pathology is hippocampal sclerosis with neuronal loss and reactive astrogliosis. Although astrocytes have emerged as potential targets for antiepileptic therapies, their role in epilepsy development remains poorly defined. Here, we combined adeno-associated virus (AAV)-mediated labeling with translating ribosomal affinity purification (TRAP) to generate astrocyte-enriched transcriptome profiles from sclerotic hippocampal regions in a mouse model of MTLE. This analysis identified a marked upregulation of insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 2 (Igfbp2) in reactive astrocytes. Functional studies revealed that astrocytic Igfbp2 increases the excitability of dentate granule cells and promotes spontaneous recurrent seizures. These findings reveal Igfbp2 as a key astrocytic modulator of hippocampal excitability and identify it as a potential therapeutic target for epilepsy.