2025-12-15 マウントサイナイ医療システム(MSHS)
<関連情報>
- https://www.mountsinai.org/about/newsroom/2025/new-ai-tool-identifies-not-just-genetic-mutations-but-the-diseases-they-may-cause
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-025-66607-w
表現型特異的モデルによる変異効果予測の有用性の拡大 Expanding the utility of variant effect predictions with phenotype-specific models
David Stein,Meltem Ece Kars,Baptiste Milisavljevic,Matthew Mort,Peter D. Stenson,Jean-Laurent Casanova,David N. Cooper,Bertrand Boisson,Peng Zhang,Avner Schlessinger & Yuval Itan
Nature Communications Published:28 November 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-025-66607-w
Abstract
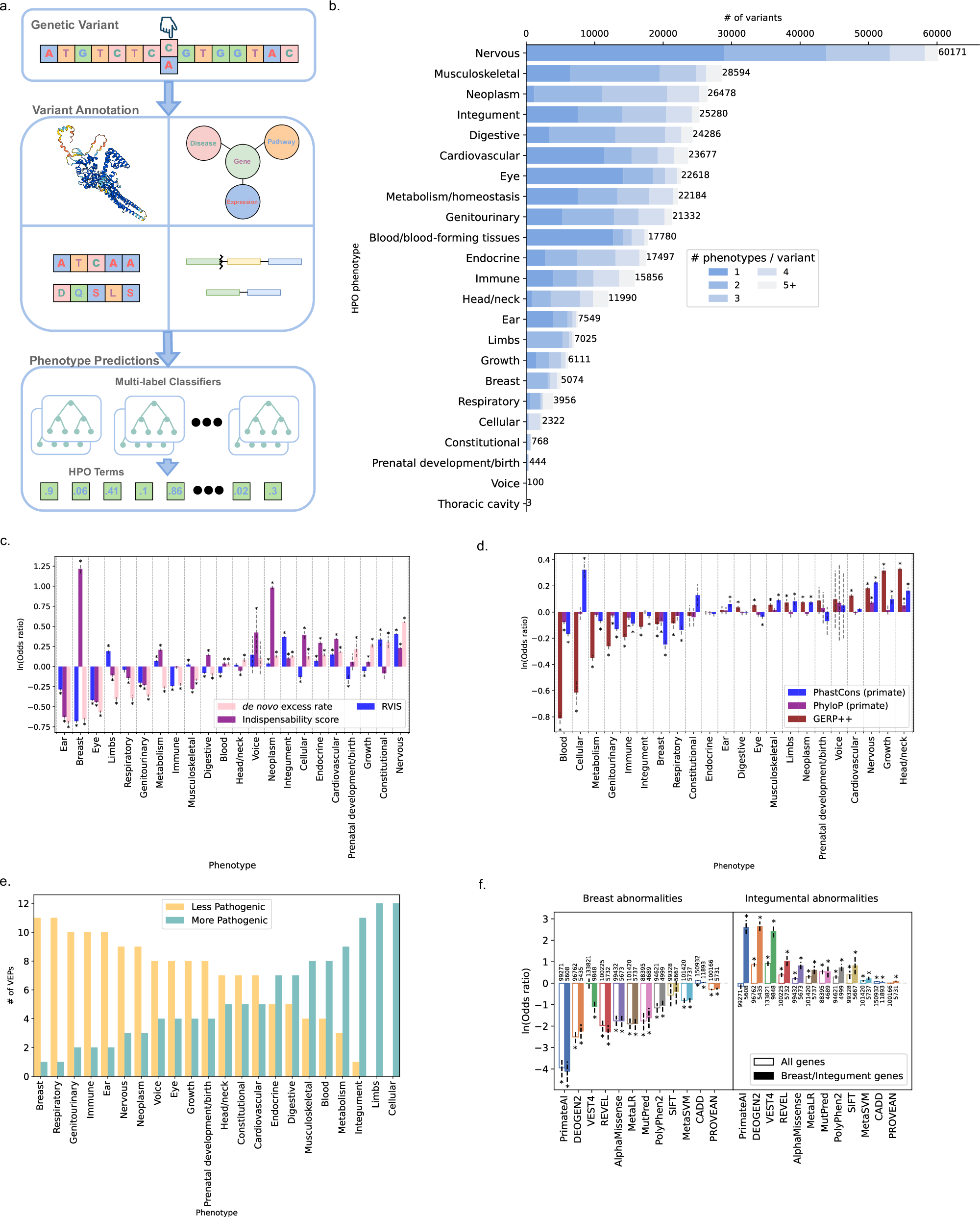
Current methods for variant effect prediction do not differentiate between pathogenic variants resulting in different disease outcomes and are restricted in application due to a focus on variants with a single molecular consequence. We have developed Variant-to-Phenotype (V2P), a multi-task, multi-output machine learning model to predict variant pathogenicity conditioned on top-level Human Phenotype Ontology disease phenotypes (n = 23) for single nucleotide variants and insertions/deletions throughout the human genome. V2P leverages a unique approach for the modeling of variant effect that incorporates resultant disease phenotypes as output and during training to improve the quality of variant disease phenotype and effect predictions, simultaneously. We describe the architecture, training strategy, and biological features contributing to V2P’s output, revealing initial characteristics underlying the relationship between disease genotype and phenotype. Moreover, we demonstrate the benefit of incorporating disease phenotypes for variant effect predictions by comparing V2P with several variant effect predictors across various high-quality evaluation datasets from manually curated databases and functional assays. Finally, we examine how V2P’s predictions result in the successful identification of pathogenic variants in real and simulated patient sequencing data, outperforming other tested methods in initial comparisons. V2P offers a complete mapping of human genetic variants to disease-phenotypes, offering a uniquely conditioned set of variant effect characterizations.