2026-01-31 筑波大学
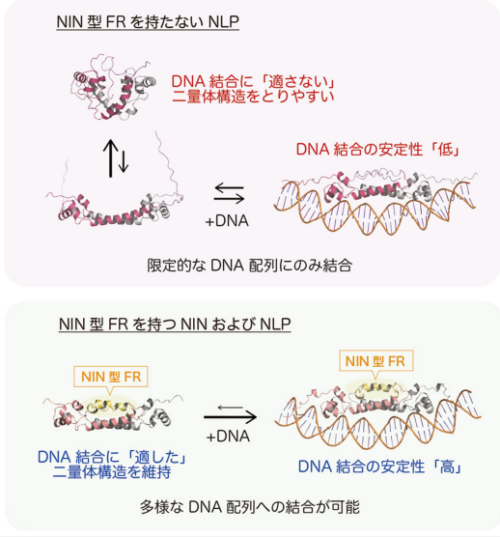
図1. NIN 型 FR を介した DNA 結合モデル NIN 型 FR を持たない典型的な NLP は、⼆量体を形成する DNA 結合ドメイン(各分⼦を⾚および灰 ⾊で図⽰)が DNA 結合に適さない⼆量体構造をとりやすく、DNA 結合時の安定性も低い。このため、限定的な DNA 配列にのみ結合する(上図)。⼀⽅、NIN 型 FR(⻩⾊で図⽰)を持つ NIN およびその祖先型の⼀部 NLP では、FR が DNA 結合ドメイン間の相互作⽤を拡張し、DNA 結合に適した⼆量体構造を維持するとともに、DNA 結合時の安定性を⾼める(下図)。その結果、典型的な NLP に⽐べて、多様な DNA 配列への結合が可能となる。
<関連情報>
- https://www.tsukuba.ac.jp/journal/biology-environment/20260131040000.html
- https://www.tsukuba.ac.jp/journal/pdf/p20260131040000.pdf
- https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/sciadv.aeb8825
根粒共生を制御する因子NINは、NLPから受け継いだモチーフによって広範なDNA結合特異性を示す The root nodule symbiosis regulator NIN exhibits broad DNA binding specificity conferred by an NLP-inherited motif
Shohei Nosaki, Momona Noda, Hiroki Onoda, Momoyo Ito, and Takuya Suzaki
Science Advances Published:30 Jan 2026
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.aeb8825
Abstract
Nitrogen-fixing root nodule symbiosis (RNS) occurs in some eudicots, including legumes, and is regulated by the transcription factor NODULE INCEPTION (NIN), derived from the NIN-LIKE PROTEIN (NLP) family. However, how the NIN protein acquired RNS-specific functions remains unclear. We identify a previously undescribed motif in Lotus japonicus NIN, located downstream of the RWP-RK domain, which we term the FR. This motif broadens NIN’s DNA binding specificity by stabilizing the RWP-RK dimer interface. nin mutants lacking the FR motif show defective nodulation and impaired nitrogen fixation. Arabidopsis NLP2 carries a NIN-type FR and shares key features with NIN. Furthermore, the NIN-type FR had already emerged before the divergence of gymnosperm and angiosperm lineages, suggesting that a specific molecular feature of NIN involved in RNS regulation was inherited from ancestral NLPs prior to the emergence of RNS.