2022-08-25 サセックス大学
研究者たちは、Smc5/6複合体の構成要素をコードするDNAに変化が生じると、原始小人症、インスリン抵抗性、LICS(肺疾患・免疫不全・染色体破壊症候群)という現在では致命的な病態に至ることを明らかにした。
この複合体はまた、いわゆる「制限因子」として働き、B型肝炎、単純ヘルペス、子宮頸がんや口腔咽頭がんの原因物質であるパピローマウイルスなどの侵入ウイルスから細胞を防御するのに役立っている。
<関連情報>
- https://www.sussex.ac.uk/research/full-news-list?id=58507
- https://academic.oup.com/nar/advance-article/doi/10.1093/nar/gkac692/6673127?login=false
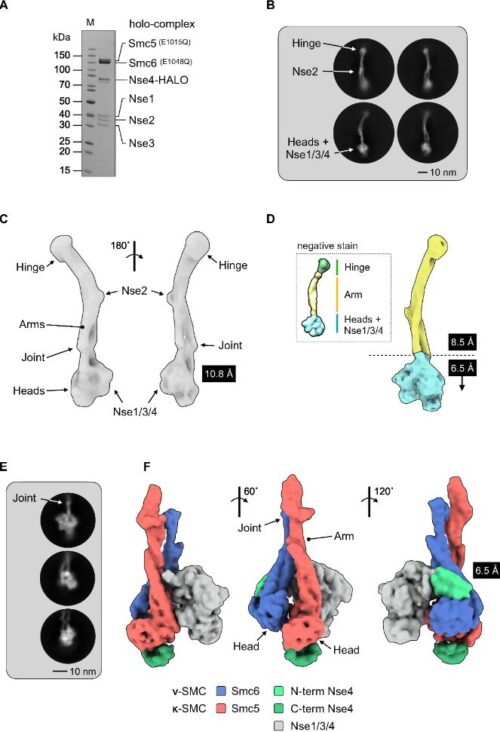
Smc5/6ホロ-コンプレックスの低温電子顕微鏡構造 Cryo-EM structure of the Smc5/6 holo-complex
Stephen T Hallett, Isabella Campbell Harry, Pascale Schellenberger, Lihong Zhou, Nora B Cronin, Jonathan Baxter, Thomas J Etheridge, Johanne M Murray, Antony W Oliver
Nucleic Acids Research Published:22 August 2022
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkac692
Abstract
The Smc5/6 complex plays an essential role in the resolution of recombination intermediates formed during mitosis or meiosis, or as a result of the cellular response to replication stress. It also functions as a restriction factor preventing viral replication. Here, we report the cryogenic EM (cryo-EM) structure of the six-subunit budding yeast Smc5/6 holo-complex, reconstituted from recombinant proteins expressed in insect cells – providing both an architectural overview of the entire complex and an understanding of how the Nse1/3/4 subcomplex binds to the hetero-dimeric SMC protein core. In addition, we demonstrate that a region within the head domain of Smc5, equivalent to the ‘W-loop’ of Smc4 or ‘F-loop’ of Smc1, mediates an important interaction with Nse1. Notably, mutations that alter the surface-charge profile of the region of Nse1 which accepts the Smc5-loop, lead to a slow-growth phenotype and a global reduction in the chromatin-associated fraction of the Smc5/6 complex, as judged by single molecule localisation microscopy experiments in live yeast. Moreover, when taken together, our data indicates functional equivalence between the structurally unrelated KITE and HAWK accessory subunits associated with SMC complexes.