2023-03-09 マックス・プランク研究所
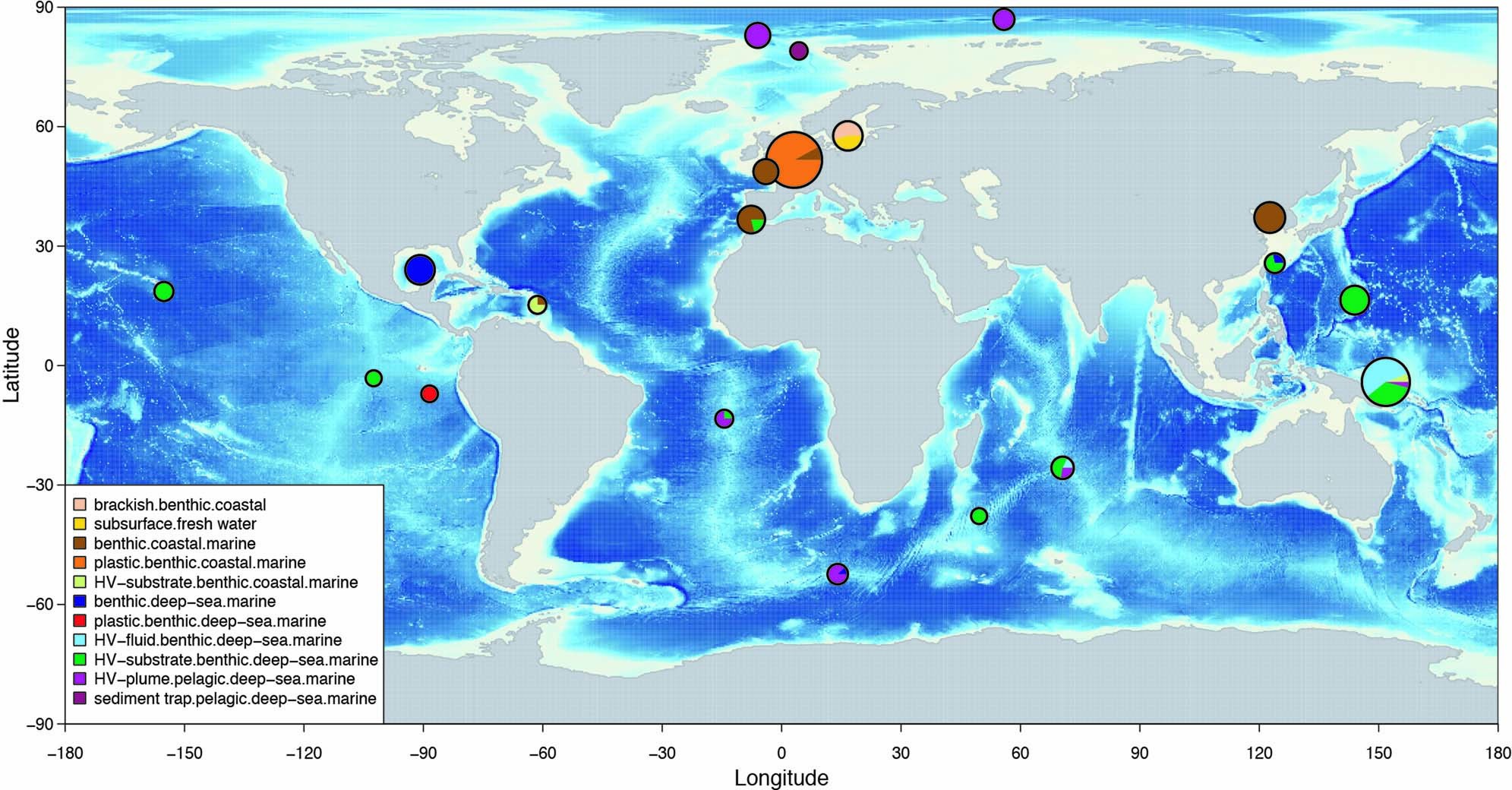
最近の研究では、低酸素環境でしか成長できないSulfurimonas属のバクテリアがハイドロサーマル・プルーム内に繁殖していることが明らかになった。バクテリアは、プルーム内の水素をエネルギー源として利用しており、酸素が豊富で低温のハイドロサーマル・プルームに生息している新しいSulfurimonas属の種が同定された。これは、Sulfurimonasが深海の生態系にとってより重要な存在である可能性があることを示唆している。
<関連情報>
- https://www.mpg.de/19982028/0309-mbio-life-in-the-smoke-of-underwater-volcanoes-154772-x?c=2249
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41564-023-01342-w
深海の酸素飽和熱水プルームにグローバルに存在する水素栄養性Sulfurimonasの存在 A hydrogenotrophic Sulfurimonas is globally abundant in deep-sea oxygen-saturated hydrothermal plumes
Massimiliano Molari,Christiane Hassenrueck,Rafael Laso-Pérez,Gunter Wegener,Pierre Offre,Stefano Scilipoti & Antje Boetius
Nature Microbiology Published:09 March 2023
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41564-023-01342-w
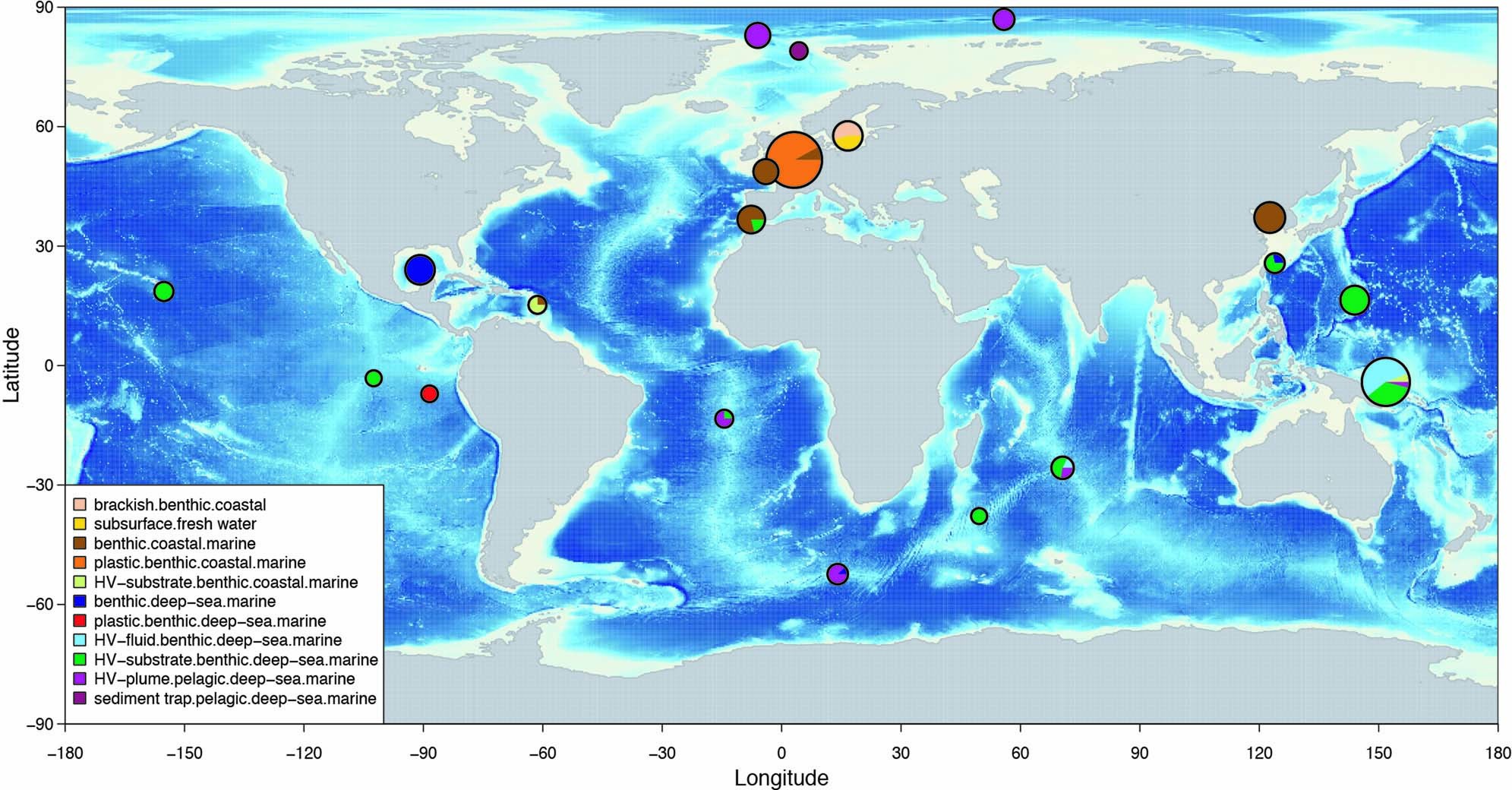
Abstract
Members of the bacterial genus Sulfurimonas (phylum Campylobacterota) dominate microbial communities in marine redoxclines and are important for sulfur and nitrogen cycling. Here we used metagenomics and metabolic analyses to characterize a Sulfurimonas from the Gakkel Ridge in the Central Arctic Ocean and Southwest Indian Ridge, showing that this species is ubiquitous in non-buoyant hydrothermal plumes at Mid Ocean Ridges across the global ocean. One Sulfurimonas species, USulfurimonas pluma, was found to be globally abundant and active in cold (<0-4 °C), oxygen-saturated and hydrogen-rich hydrothermal plumes. Compared with other Sulfurimonas species, US. pluma has a reduced genome (>17%) and genomic signatures of an aerobic chemolithotrophic metabolism using hydrogen as an energy source, including acquisition of A2-type oxidase and loss of nitrate and nitrite reductases. The dominance and unique niche of US. pluma in hydrothermal plumes suggest an unappreciated biogeochemical role for Sulfurimonas in the deep ocean.