2024-08-20 カロリンスカ研究所(KI)
<関連情報>
- https://news.ki.se/precision-therapy-for-metastatic-prostate-cancer-improves-survival
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41591-024-03204-2
転移性前立腺がんにおけるアンドロゲン受容体経路阻害薬とタキサン系薬剤:アウトカム適応無作為化プラットフォーム試験 Androgen receptor pathway inhibitors and taxanes in metastatic prostate cancer: an outcome-adaptive randomized platform trial
Bram De Laere,Alessio Crippa,Andrea Discacciati,Berit Larsson,Maria Persson,Susanne Johansson,Sanne D’hondt,R. Bergström,Venkatesh Chellappa,Markus Mayrhofer,Mahsan Banijamali,Anastasijia Kotsalaynen,Céline Schelstraete,Jan Pieter Vanwelkenhuyzen,Marie Hjälm-Eriksson,Linn Pettersson,Anders Ullén,Nicolaas Lumen,Gunilla Enblad,Camilla Thellenberg Karlsson,Elin Jänes,Johan Sandzén,Peter Schatteman,Maria Nyre Vigmostad,… Johan Lindberg
Nature Medicine Published:20 August 2024
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-024-03204-2
Abstract
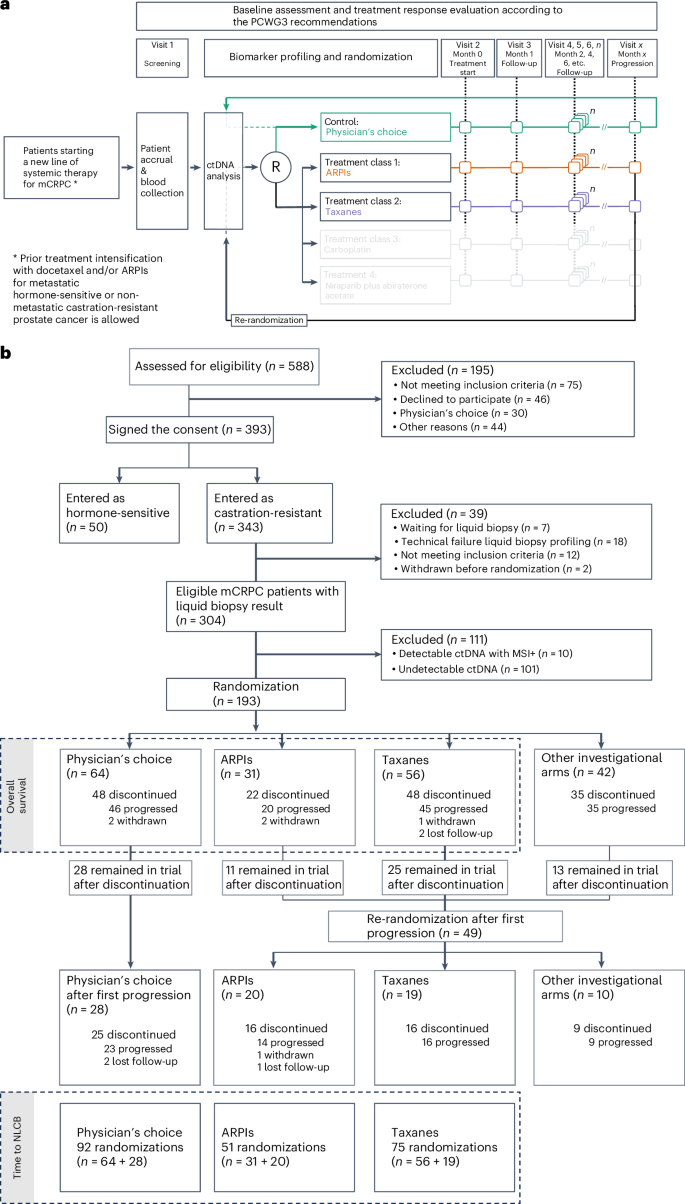
ProBio is the first outcome-adaptive platform trial in prostate cancer utilizing a Bayesian framework to evaluate efficacy within predefined biomarker signatures across systemic treatments. Prospective circulating tumor DNA and germline DNA analysis was performed in patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer before randomization to androgen receptor pathway inhibitors (ARPIs), taxanes or a physician’s choice control arm. The primary endpoint was the time to no longer clinically benefitting (NLCB). Secondary endpoints included overall survival and (serious) adverse events. Upon reaching the time to NLCB, patients could be re-randomized. The primary endpoint was met after 218 randomizations. ARPIs demonstrated ~50% longer time to NLCB compared to taxanes (median, 11.1 versus 6.9 months) and the physician’s choice arm (median, 11.1 versus 7.4 months) in the biomarker-unselected or ‘all’ patient population. ARPIs demonstrated longer overall survival (median, 38.7 versus 21.7 and 21.8 months for taxanes and physician’s choice, respectively). Biomarker signature findings suggest that the largest increase in time to NLCB was observed in AR (single-nucleotide variant/genomic structural rearrangement)-negative and TP53 wild-type patients and TMPRSS2–ERG fusion-positive patients, whereas no difference between ARPIs and taxanes was observed in TP53-altered patients. In summary, ARPIs outperform taxanes and physician’s choice treatment in patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer with detectable circulating tumor DNA. ClinicalTrials.gov registration: NCT03903835.