2025-07-09 東京大学
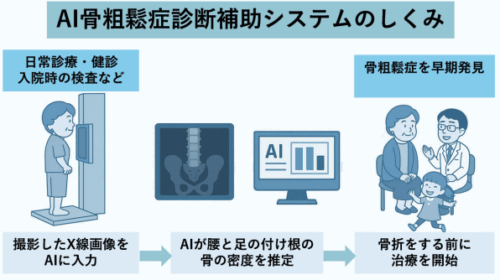
図 1:AI 骨粗鬆症診断補助システムの概要 1 枚の X 線画像データのみから腰椎および大腿骨近位部の骨密度推定値を演算する
<関連情報>
- https://www.h.u-tokyo.ac.jp/press/20250709.html
- https://www.h.u-tokyo.ac.jp/press/__icsFiles/afieldfile/2025/07/09/release_20250709_1.pdf
腰椎X線前後画像を用いた人工知能による腰椎・大腿骨BMD推定システムの開発 Development of Artificial Intelligence-Assisted Lumbar and Femoral BMD Estimation System Using Anteroposterior Lumbar X-Ray Images
Toru Moro, Noriko Yoshimura, Taku Saito, Hiroyuki Oka, Sigeyuki Muraki, Toshiko Iidaka, Takeyuki Tanaka, Kumiko Ono, Hisatoshi Ishikura, Naoya Wada, Kenichi Watanabe …
Journal of Orthopaedic Research Published: 09 July 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1002/jor.70000
ABSTRACT
The early detection and treatment of osteoporosis and prevention of fragility fractures are urgent societal issues. We developed an artificial intelligence-assisted diagnostic system that estimated not only lumbar bone mineral density but also femoral bone mineral density from anteroposterior lumbar X-ray images. We evaluated the performance of lumbar and femoral bone mineral density estimations and the osteoporosis classification accuracy of an artificial intelligence-assisted diagnostic system using lumbar X-ray images from a population-based cohort. The artificial neural network consisted of a deep neural network for estimating lumbar and femoral bone mineral density values and classifying lumbar X-ray images into osteoporosis categories. The deep neural network was built by training dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry-derived lumbar and femoral bone mineral density values as the ground truth of the training data and preprocessed X-ray images. Five-fold cross-validation was performed to evaluate the accuracy of the estimated BMD. A total of 1454 X-ray images from 1454 participants were analyzed using the artificial neural network. For the bone mineral density estimation performance, the mean absolute errors were 0.076 g/cm2 for the lumbar and 0.071 g/cm2 for the femur between dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry-derived and artificial intelligence-estimated bone mineral density values. The classification performances for the lumbar and femur of patients with osteopenia, in terms of sensitivity, were 86.4% and 80.4%, respectively, and the respective specificities were 84.1% and 76.3%.
Clinical Significance
The system was able to estimate the bone mineral density and classify the osteoporosis category of not only patients in clinics or hospitals but also of general inhabitants.