2025-07-11 幌延地圏環境研究所
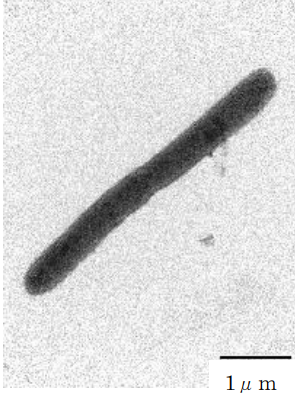
図 1. 水素を生成する Gaoshiqia hydrogeniformans Z1-71T株の電子顕微鏡写真
<関連情報>
- https://www.h-rise.jp/info/detail.php?pid=2159600561175
- https://www.h-rise.jp/cgi-bin/upload/kenkyu/file1_1752192419_Z1-71_Press.pdf
深部珪藻質頁岩層から分離された新規水素生成細菌Gaoshiqia hydrogeniformans sp.
Gaoshiqia hydrogeniformans sp. nov., a novel hydrogen-producing bacterium isolated from a deep diatomaceous shale formation
Akio Ueno, Kiyoshi Sato, Shuji Tamamura, Takuma Murakami, Hidenori Inomata, Satoshi Tamazawa, Yuki Amano,, Kazuya Miyakawa,, Takeshi Naganuma and Toshifumi Igarashi
International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology Published: 04 June 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.006802
In the deep subsurface Miocene groundwater of Horonobe, Hokkaido, Japan, we isolated strain Z1-71ᵀ, an obligately anaerobic, Gram-stain-negative, non-motile bacterium with rod-shaped morphology (2.7–4.8 µm × 0.4 µm). This strain could grow at 10–42 °C (optimum, 30–35 °C), over a pH range of 6.0–9.0 (optimum, pH 7.0–7.2) and in the presence of 0–30 g l-1 NaCl (optimum, 5–15 g l-1). Physiologically, strain Z1-71ᵀ displayed positive catalase activity but negative oxidase reaction, with notable hydrogen production during d-glucose metabolism. Chemotaxonomic analysis revealed MK-7 as the sole respiratory quinone, while cellular lipid profiling identified four unidentified polar lipids, one unidentified phospholipid, one unidentified aminolipid and one unidentified glycolipid. The predominant fatty acids comprised C17:0 (23.4%), C17:1 ω6c (13.8%), anteiso-C15 :0 (6.9%) and iso-C17:0 3-OH (6.6%). Genomic characterization determined a genome size of 5.7 Mb with a G+C content of 45.9 mol%. Comprehensive phylogenetic analysis of 16S rRNA gene sequences positioned strain Z1-71ᵀ within the family Prolixibacteraceae, showing the highest sequence similarity to Gaoshiqia sediminis A06T (95.0%), followed by Mangrovibacterium diazotrophicum SCSIO N0430T (94.6%), Mangrovibacterium lignilyticum BM_7T (94.3%) and Mangrovibacterium marinum FA423T (93.6%). Digital DNA–DNA hybridization and orthologous average nucleotide identity tool using USEARCH (OrthoANIu) analyses between strain Z1-71ᵀ and G. sediminis A06T yielded values of 20.7% and 75.8%, respectively, confirming genomic distinction. Based on these phylogenetic and phenotypic characteristics, we propose strain Z1-71ᵀ (=DSM 117644ᵀ=JCM 36072ᵀ) as the type strain of a novel species, Gaoshiqia hydrogeniformans sp. nov. This discovery not only expands our understanding of microbial diversity in deep terrestrial subsurface environments but also highlights the ecological significance of hydrogen-producing anaerobes in these previously underexplored habitats.