2022-05-03 イリノイ大学アーバナ・シャンペーン校
新しい研究では、植物の健康を促進することが知られている土壌細菌の存在下または非存在下で、異なる品種のトウモロコシが草食動物にどのように反応するかを比較し、トウモロコシ植物の化学的シグナル伝達能力に寄与する要因を探った。
<関連情報>
- https://news.illinois.edu/view/6367/1075886635
- https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmicb.2022.826635/full
揮発性有機化合物を介した草食動物の保護は、バチルス・アルティトゥジニスに富む細菌群ではなく、トウモロコシの遺伝子型に影響される。 Herbivory Protection via Volatile Organic Compounds Is Influenced by Maize Genotype, Not Bacillus altitudinis-Enriched Bacterial Communities
Sierra S. Raglin, Angela D. Kent and Esther N. Ngumbi
Frontiers in Microbiology Published:02 May 2022
DOI:https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2022.826635
Abstract
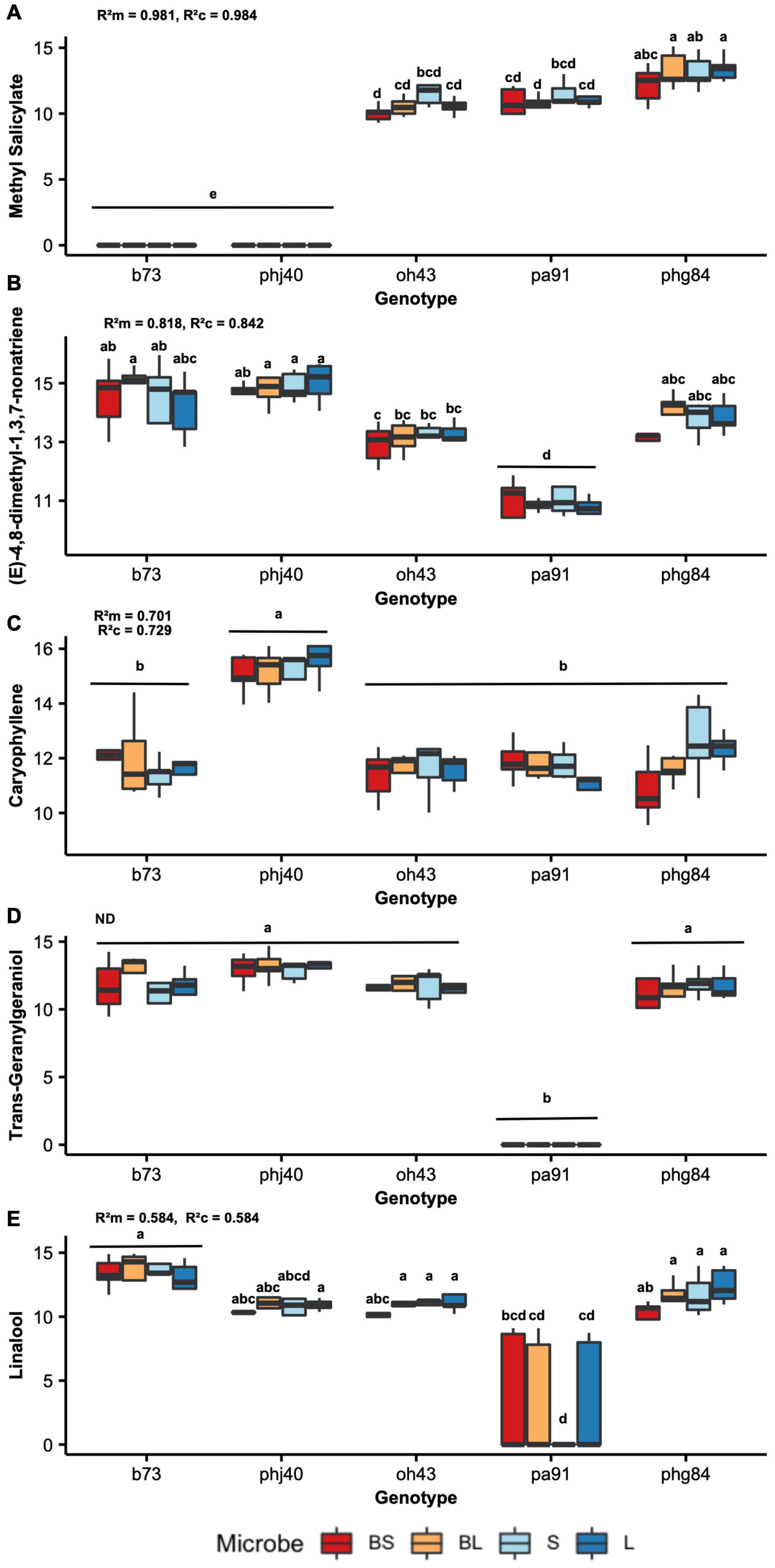
Belowground, plants interact with beneficial soil microbes such as plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR). PGPR are rhizosphere bacteria that colonize roots and elicit beneficial effects in plants such as improved plant growth, pathogen resistance, abiotic stress tolerance, and herbivore protection. Treatment of plants with PGPR has been shown to trigger the emission of volatile organic compounds (VOCs). Volatile emissions can also be triggered by herbivory, termed herbivore-induced plant volatiles (HIPV), with important ramifications for chemical-mediated plant and insect interactions. Much of our current understanding of PGPR and herbivore-induced volatiles is based on studies using one plant genotype, yet domestication and modern breeding has led to the development of diverse germplasm with altered phenotypes and chemistry. In this study, we investigated if volatile emissions triggered by PGPR colonization and herbivory varies by maize genotype and microbial community assemblages. Six maize genotypes representing three decades of crop breeding and two heterotic groups were used, with four microbiome treatments: live or sterilized soil, with or without a Bacillus inoculant. Soil sterilization was used to delay microbiome establishment, resulting in low-diversity treatments. At planting, maize seeds were inoculated with PGPR Bacillus altitudinis AP-283 and grown under greenhouse conditions. Four weeks post planting, plants were subjected to feeding by third instar Helicoverpa zea (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) larvae. Volatiles were collected using solid phase microextraction and analyzed with gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Illumina NovaSeq 16S rRNA amplicon sequencing was carried out to characterize the rhizosphere microbiome. Maize genotype significantly influenced total volatile emissions, and relative abundance of volatile classes. We did not document a strong influence of microbe treatment on plant VOC emissions. However, inoculating plants with PGPR improved plant growth under sterile conditions. Taken together, our results suggest that genotypic variation is the dominant driver in HIPV composition and individual HIPV abundances, and any bacterial-mediated benefit is genotype and HIPV-specific. Therefore, understanding the interplay of these factors is necessary to fully harness microbially-mediated benefits and improve agricultural sustainability.