2025-08-04 カナダ・ブリティッシュコロンビア大学 (UBC)
ChatGPT:
<関連情報>
Vibrio pectenicida 株FHCF-3は、ヒトデの衰弱病の病原体である Vibrio pectenicida strain FHCF-3 is a causative agent of sea star wasting disease
Melanie B. Prentice,Grace A. Crandall,Amy M. Chan,Katherine M. Davis,Paul K. Hershberger,Jan F. Finke,Jason Hodin,Andrew McCracken,Colleen T. E. Kellogg,Rute B. G. Clemente-Carvalho,Carolyn Prentice,Kevin X. Zhong,C. Drew Harvell,Curtis A. Suttle & Alyssa-Lois M. Gehman
Nature Ecology & Evolution Published:04 August 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41559-025-02797-2
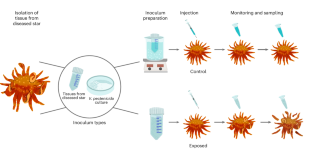
Abstract
More than 10 years following the onset of the sea star wasting disease (SSWD) epidemic, affecting over 20 asteroid species from Mexico to Alaska, the causative agent has been elusive. SSWD killed billions of the most susceptible species, sunflower sea stars (Pycnopodia helianthoides), initiating a trophic cascade involving unchecked urchin population growth and the widespread loss of kelp forests. Identifying the causative agent underpins the development of recovery strategies. Here we induced disease and subsequent mortality in exposure experiments using tissue extracts, coelomic fluid and effluent water from wasting sunflower sea stars, with no mortality in controls. Deep sequencing of diseased sea star coelomic fluid samples from experiments and field outbreaks revealed a dominant proportion of reads assigned to the bacterium Vibrio pectenicida. Fulfilling Koch’s postulates, V. pectenicida strain FHCF-3, cultured from the coelomic fluid of a diseased sunflower sea star, caused disease and mortality in exposed sunflower sea stars, demonstrating that it is a causative agent of SSWD. This discovery will enable recovery efforts for sea stars and the ecosystems affected by their decline by facilitating culture-based experimental research and broad-scale screening for pathogen presence and abundance in the laboratory and field.


