2025-08-08 京都大学
<関連情報>
- https://www.kyoto-u.ac.jp/ja/research-news/2025-08-08
- https://www.kyoto-u.ac.jp/sites/default/files/2025-08/web_2508_PNAS_Hagiwara_webj-fe2ee944930d8e06e569c0ef953bfa3f.pdf
- https://www.pnas.org/doi/10.1073/pnas.2500006122
α2Bアドレナリン受容体を標的とした経口鎮痛剤の発見と開発 Discovery and development of an oral analgesic targeting the α2B adrenoceptor
Masayasu Toyomoto, Takashi Kurihara, Takayuki Nakagawa, +16 , and Masatoshi Hagiwara
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences Published:August 7, 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2500006122
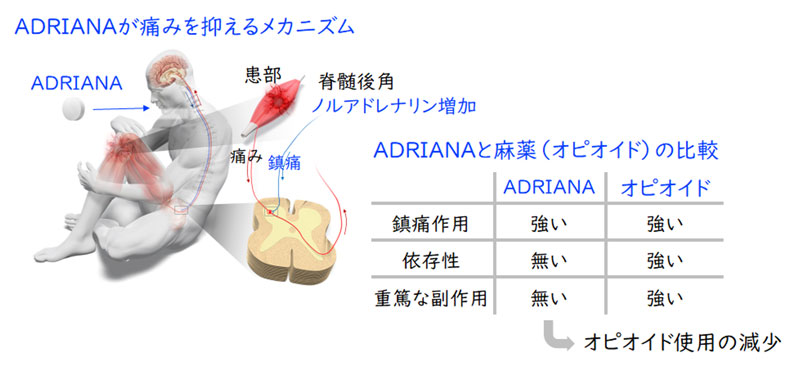
Significance
Control of pain is a global social health issue because severe pain strongly affects patients’ quality of life. Although opioids are the strongest painkillers, continuous use of opioids often leads to addiction with numerous adverse effects, including respiratory depression, constipation, and hyperalgesia. An emerging alternative to opioid-based analgesics is dexmedetomidine, an α2-adrenergic receptor agonist. We found that administration of an α2B-specific antagonist, adrenergic inducer of analgesia (ADRIANA), induced noradrenaline release in the spinal dorsal horn and suppressed pain through an α2A-dependent pathway without causing hemodynamic instability. ADRIANA did not cause addiction or any behavioral change in mice and monkeys. A phase I/II clinical trial of the ADRIANA oral tablet is underway to test its effectiveness in reducing postoperative pain.
Abstract
Noradrenaline is a major monoaminergic neurotransmitter involved in pain modulation through an α2A-adrenergic receptor. Hence, α2-adrenergic agonists such as clonidine and dexmedetomidine exhibit analgesic and opioid-sparing effects. However, their use is restricted to hospital settings due to potential risks of acute hypertension/hypotension and bradycardia. Here, we report that (Z)-1-(3-ethyl-5-fluorobenzo[d] thiazol-2(3H)-ylidene)propan-2-one [adrenergic inducer of analgesia (ADRIANA)], a newly identified α2B subtype-specific antagonist, specifically promotes noradrenaline release in the murine spinal dorsal horn and produces analgesic effects by stimulating the α2A-dependent pain inhibitory pathway. Orally administered ADRIANA has potent analgesic effects in several nociceptive pain models of mice and nonhuman primates without cardiovascular effects. Mice with genetic loss of the α2B adrenoceptor showed normal responses to mechanical pain, but the analgesic effect of ADRIANA was not significantly detected. These findings reveal that the α2B adrenoceptor is a promising target for nonopioid analgesics through the activation of the α2A-dependent descending pathway.