2025-08-28 産業技術総合研究所
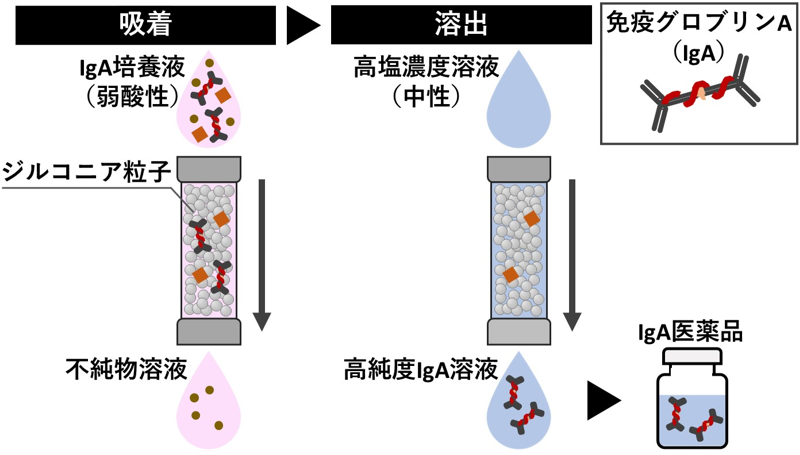
概要図 ジルコニアカラムを用いたIgAの精製のイメージ
<関連情報>
- https://www.aist.go.jp/aist_j/press_release/pr2025/pr20250828/pr20250828.html
- https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acsami.5c11319
リン酸塩被覆メソポーラスジルコニア粒子を用いた免疫グロブリンAの精製 Purification of Immunoglobulin A Using Mesoporous Zirconia Particles Coated with Phosphate
Shogo Kanoh,Koshiro Tabata,Shinji Saito,Erika Onuma,Hatsuho Usuda,Kentaro Shiraki,Katsuya Kato,and Atsushi Hirano
ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces Published August 27, 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.5c11319
Abstract
Immunoglobulin A (IgA) is the most abundant antibody in the human body and plays a critical role in defending against bacteria and viruses that invade through mucosal surfaces. Leveraging this property, recombinant IgA has been developed as a preventive drug for infectious diseases such as COVID-19, influenza, and tuberculosis. Recombinant IgA is typically purified using columns packed with protein-immobilized resins, such as jacalin, Protein L, or nanobody-based materials. However, these methods have several drawbacks, including high costs due to expensive resins and mobile phases, the need for multiple purification steps, and the potential leakage of immobilized proteins. To address these issues, the present study proposes an alternative IgA purification method using zirconia (ZrO2) particles. Purification was performed for three forms of IgA─monomeric, dimeric, and secretory component-bound IgA─using both batch adsorption and chromatography. All three forms were successfully purified with high purity. The method employs phosphate buffers at mildly acidic and neutral pH as the mobile phase, which helps preserve the structure of IgA. Because ZrO2 particles are both cost-effective and chemically and mechanically robust, the proposed method overcomes the limitations associated with conventional protein-immobilized resins in IgA purification.