2025-09-08 東京科学大学
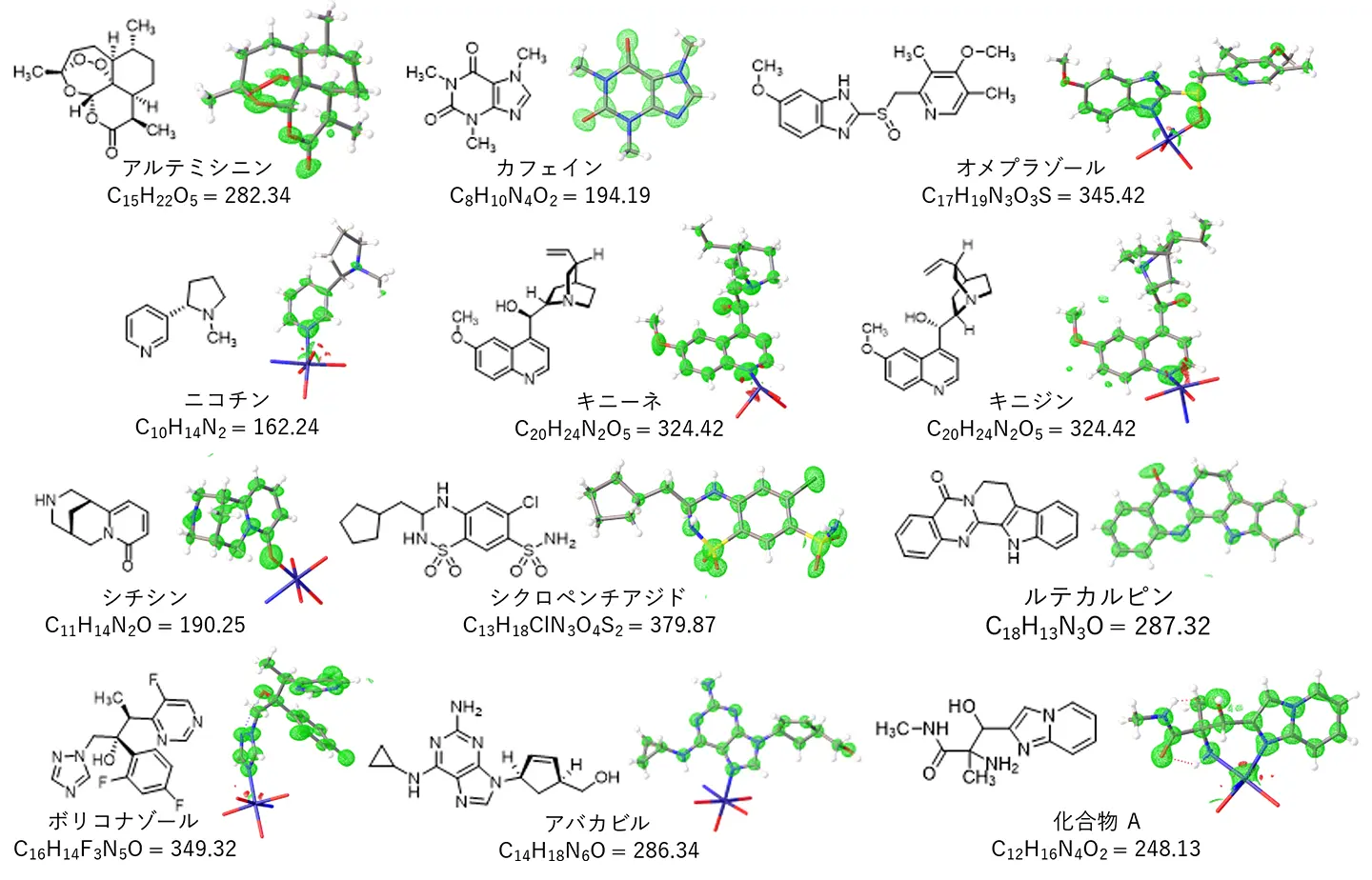
図1. 開発されたMOFにより解析された求核性化合物の構造式と観測された電子密度マップ。電子密度により化合物の構造を判定できる。
<関連情報>
- https://www.isct.ac.jp/ja/news/ipaznbm1wmef
- https://www.isct.ac.jp/plugins/cms/component_download_file.php?type=2&pageId=&contentsId=1&contentsDataId=2186&prevId=&key=b77e2198b55e589320f078e5788b86af.pdf
- https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/jacs.5c07192
金属有機構造体における相乗的な配位と水素結合による求核性化合物の構造解明 Structural Elucidation of Nucleophilic Compounds through Synergistic Coordination and Hydrogen Bonding in a Metal–Organic Framework
Tomoki Nakagawa,Yuki Wada,Bun Chan,Taichi Baba,Kengo Hanaya,Yuta Koseki,Ryuji Asano,Katsuyuki Aoki,Pavel M. Usov,and Masaki Kawano
Journal of the American Chemical Society Published July 31, 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.5c07192
Abstract
This study presents the development of a novel metal–organic framework (MOF) denoted as APF-80, suitable for the structural analysis of nucleophilic compounds that have traditionally been challenging to analyze using the crystalline sponge method. It was synthesized using a new mixed-substituent hexaazaphenalene ligand (344-TPHAP) featuring both 3-pyridyl and 4-pyridyl groups. This framework demonstrated remarkable stability toward nucleophilic molecules, which could be captured inside the pores through a synergistic combination of coordination and hydrogen-bonding interactions. APF-80 was successfully applied to determine the structures of 12 bioactive molecules, including naturally occurring alkaloids and pharmaceutical compounds. The host–guest interaction modes observed inside the resulting structures were classified into five distinct types. Binding energy calculations revealed that the guest site energies positively correlated with the crystallographic occupancies and the corresponding interaction types. This multimodal capture mechanism enabled the precise structural analysis of nucleophilic compounds under mild conditions, expanding the scope of molecules that can be analyzed by the crystalline sponge method.