2025-09-15 スイス連邦工科大学ローザンヌ校(EPFL)
<関連情報>
- https://actu.epfl.ch/news/mapping-the-lipid-blueprint-of-life-in-4d/
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41592-025-02771-7
統一質量イメージングによる脊椎動物発生の脂質体マッピング Unified mass imaging maps the lipidome of vertebrate development
Halima Hannah Schede,Leila Haj Abdullah Alieh,Laurel Ann Rohde,Antonio Herrera,Anjalie Schlaeppi,Guillaume Valentin,Alireza Gargoori Motlagh,Albert Dominguez Mantes,Chloe Jollivet,Jonathan Paz-Montoya,Laura Capolupo,Irina Khven,Andrew C. Oates,Giovanni D’Angelo & Gioele La Manno
Nature Methods Published:03 September 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41592-025-02771-7
Abstract
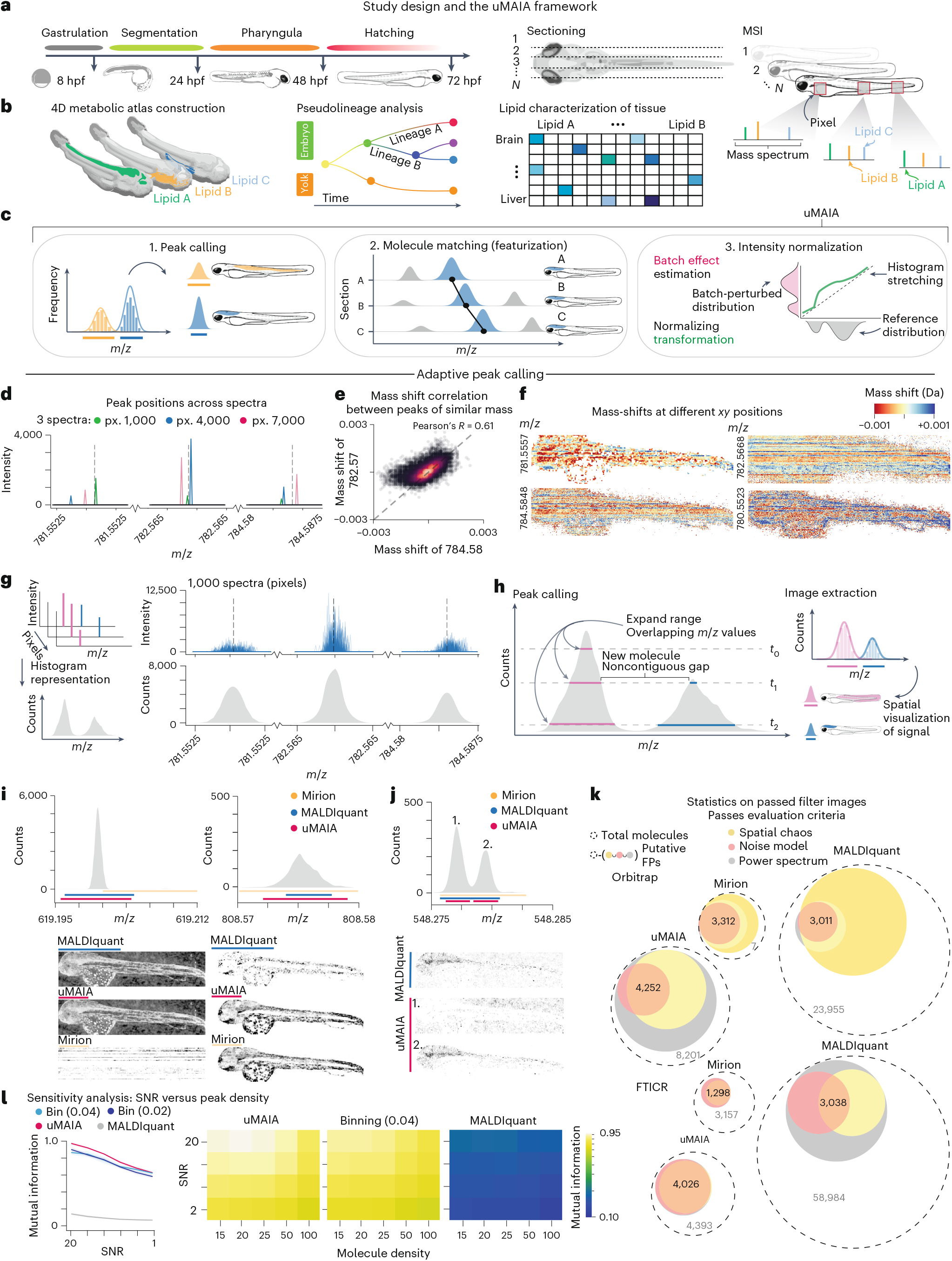
Embryo development entails the formation of anatomical structures with distinct biochemical compositions. Compared with the wealth of knowledge on gene regulation, our understanding of metabolic programs operating during embryogenesis is limited. Mass spectrometry imaging (MSI) has the potential to map the distribution of metabolites across embryo development. Here we established uMAIA, an analytical framework for the joint analysis of large MSI datasets, which enables the construction of multidimensional metabolomic atlases. Employing this framework, we mapped the four-dimensional (4D) distribution of over a hundred lipids at micrometric resolution in Danio rerio embryos. We discovered metabolic trajectories that unfold in concert with morphogenesis and revealed spatially organized biochemical coordination overlooked by bulk measurements. Interestingly, lipid mapping revealed unexpected distributions of sphingolipid and triglyceride species, suggesting their involvement in pattern establishment and organ development. Our approach empowers a new generation of whole-organism metabolomic atlases and enables the discovery of spatially organized metabolic circuits.