2025-09-19 愛媛大学
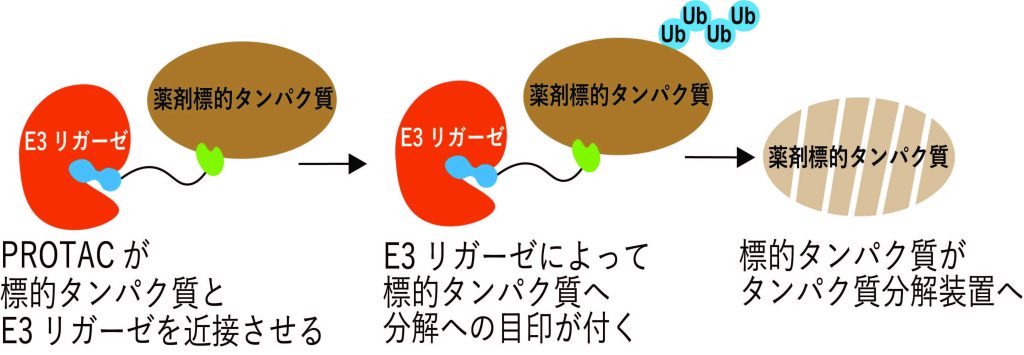
PROTAC が働く仕組み
<関連情報>
- https://www.ehime-u.ac.jp/data_relese/pr_20250919_pros/
- https://www.ehime-u.ac.jp/wp-content/uploads/2025/09/pr_20250919_pros.pdf
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s42003-025-08761-x
AirIDを用いたCRBNまたはVHL結合体を有するヘテロバイファンクショナル化合物に対する細胞内近接標的タンパク質探索法 In-cell proximity target validation methods for heterobifunctional molecules with CRBN- or VHL-binder using AirID
Kohdai Yamada,Satoshi Yamanaka,Hiroyuki Yamakoshi,Aki Kohyama,Yoshiharu Iwabuchi,Hidetaka Kosako & Tatsuya Sawasaki
Communications Biology Published:30 August 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s42003-025-08761-x
Abstract
Heterobifunctional molecules, such as proteolysis-targeting and autophagy-targeting chimera, represent new drug concepts. They are composed of two protein binders that can induce proximity interactions between two proteins and protein catalysis. Currently, cereblon (CRBN)- and von Hippel-Lindau (VHL)-binders with thalidomide- and VH032-backbones are widely used as E3 ligase binders. Here, we developed a method to validate proteins that interact with heterobifunctional molecules in cells using AirID, a proximity biotinylation enzyme. Interactome of target proteins was validated for six heterobifunctional molecules. ThBD-AirID, a fusion of the thalidomide-binding domain (ThBD) of CRBN and AirID, effectively biotinylated the target proteins. AirID fused to full-length VHL also exhibited highly effective biotinylation. Heterobifunctional molecules with the same target binder but different E3 binders showed different proximity interactome profiles in cells. Analysis using ThBD-AirID revealed a nuclear interaction between androgen receptor and ARV-110. AirID-fused ThBD and VHL could be useful for validating the heterobifunctional molecular interactome in cells.


