2025-11-03 カリフォルニア大学バークレー校(UCB)
Web要約 の発言:

A cardiac microphysiological system under fluorescent lighting with fluidic tubing. This heart-on-a-chip allows the screening and discovery of lipid nanoparticles that can effectively deliver gene therapies to the heart. (Image courtesy of the researchers)
<関連情報>
- https://engineering.berkeley.edu/news/2025/11/heart-on-a-chip-may-lead-to-new-treatments-for-heart-failure/
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41551-025-01523-4
脂質ナノ粒子-mRNA複合体をスクリーニングするための微小生理学的システムは、生体内での心臓トランスフェクションの有効性を予測する A microphysiological system for screening lipid nanoparticle-mRNA complexes predicts in vivo heart transfection efficacy
Gabriel Neiman,Mauro W. Costa,Hesong Han,Sheng Zhao,Tammy K. Ng,Brian Siemons,Tomohiro Nishino,Yu Huang,Shyam Lal,Kenneth Wu,Luke M. Judge,Bruce R. Conklin,Deepak Srivastava,Niren Murthy & Kevin E. Healy
Nature Biomedical Engineering Published:03 November 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41551-025-01523-4
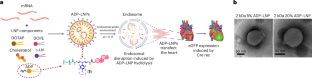
Abstract
Gene transfection via lipid nanoparticle (LNP)-mRNA complexes have tremendous potential for treating cardiac diseases. However, the transfection efficiency is poor and there is a lack of in vitro screening systems that predict transfection efficacy. Here we demonstrate a method for identifying LNP-mRNA complexes that diffuse efficiently within 3D cardiac micromuscles and transfect cardiomyocytes with high efficiency, using a phenotypic cardiac microphysiological system (MPS) constructed from a human induced pluripotent stem cell cardiomyocytes Cre-reporter line. LNP formulations containing an acid-degradable PEG–lipid had enhanced diffusion and gene editing efficiency in the cardiac MPS. The in vivo delivery of LNP-mRNA complexes, including luciferase and CRE mRNA, into Ai6 mice confirmed the cardiac MPS screening outcomes. Acid-degradable PEG-LNPs achieved notably superior transfection in the heart with reduced off-target liver uptake compared with standard LNP formulations. The cardiac MPS showed strong LNP transfection in vitro and pinpointed a promising formulation for in vivo mRNA delivery to the heart.


