2026-01-13 産業技術総合研究所
※原論文の図を引用・改変したものを使用しています。
<関連情報>
- https://www.aist.go.jp/aist_j/press_release/pr2026/pr20260113/pr20260113.html
- https://advanced.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/advs.202514735
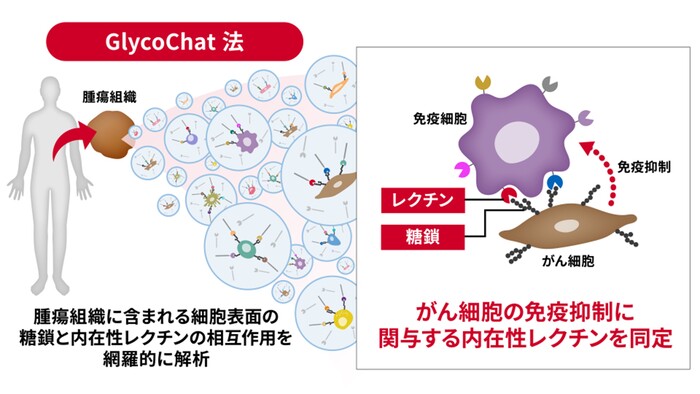
GlycoChatが膵臓癌の腫瘍微小環境におけるグリカン-レクチン回路を解明 GlycoChat Uncovers Glycan–Lectin Circuits in the Tumor Microenvironment of Pancreatic Cancer
Dinh Xuan Tuan Anh, Sunanda Keisham, Arun Burramsetty, Lalhaba Oinam, Koichiro Kumano, Akihiro Kuno, Osamu Shimomura, Tatsuya Oda, Hiroaki Tateno
Advanced Science Published: 14 January 2026
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.202514735
ABSTRACT
Aberrant glycosylation is a hallmark of cancer progression, yet its functional implications within the tumor microenvironment (TME) remain poorly understood. Here, a single-cell glycomic profiling strategy was applied to tumor tissues from patients with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC), enabling the identification of cell-type-specific glycome signatures and their dynamic alterations during the transition from classical to basal-like cancer subtypes. To systematically decode glycan-mediated communication in the TME, an analytical framework termed GlycoChat was developed for mapping global glycan–lectin circuits at single-cell resolution. GlycoChat identified CLEC10A and SIGLEC3 as lectin receptors expressed on tumor-associated macrophages that interact with cancer cell surface glycans. Functional assays demonstrated that cancer cells promote differentiation of immunosuppressive macrophages and impair phagocytic activity through interactions with CLEC10A and SIGLEC3. This study establishes GlycoChat as a powerful tool for dissecting glycan–lectin circuits in complex TME and highlights glyco-immune checkpoints as potential targets for therapeutic intervention in PDAC.


