2022-11-17 ミネソタ大学
研究チームは、COVID-19診断モデルを用いて、単一サイトと3クライアントの連携モデルのパフォーマンスを比較した。彼らは、パーソナライズされた連合学習が、内部および外部で検証されたアルゴリズムの両方を開発する機会を提供する可能性があることを発見した。
全ての機械学習手法は、より真のグローバル分布に近いデータを提供するデータにアクセスする能力から大きな恩恵を受けるので、連合学習は、強力で正確、安全、堅牢かつ不偏なモデルを得るための有望なアプローチである。
<関連情報>
- https://med.umn.edu/news-events/research-brief-evaluating-use-new-ai-technology-diagnosing-covid-19
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36214629/
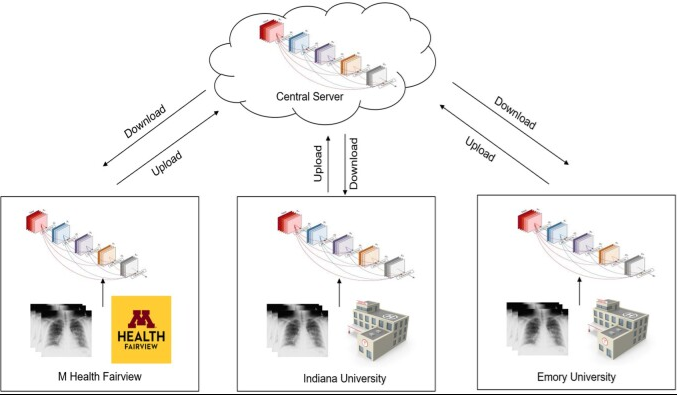
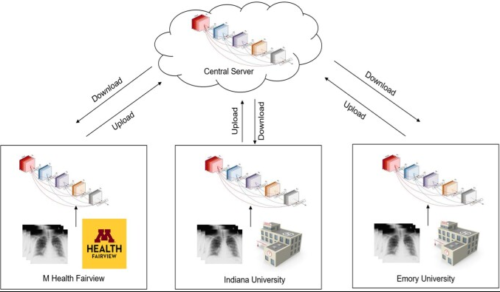
欧米の42病院の胸部X線写真を用いたCOVID-19診断のためのフェデレーション ラーニング バリエーションの評価 Evaluation of Federated Learning Variations for COVID-19 diagnosis using Chest Radiographs from 42 US and European hospitals
Le Peng, Gaoxiang Luo, Andrew Walker, Zachary Zaiman, Emma K Jones, Hemant Gupta, Kristopher Kersten, John L Burns, Christopher A Harle, Tanja Magoc, Benjamin Shickel, Scott D Steenburg, Tyler Loftus, Genevieve B Melton, Judy Wawira Gichoya, Ju Sun, Christopher J Tignanelli
Journal of the American Medical Informatics Association Published:2022 Oct 10
DOI: 10.1093/jamia/ocac188
Abstract
Objective: Federated learning (FL) allows multiple distributed data holders to collaboratively learn a shared model without data sharing. However, individual health system data are heterogeneous. “Personalized” FL variations have been developed to counter data heterogeneity, but few have been evaluated using real-world healthcare data. The purpose of this study is to investigate the performance of a single-site versus a 3-client federated model using a previously described COVID-19 diagnostic model. Additionally, to investigate the effect of system heterogeneity, we evaluate the performance of 4 FL variations.
Materials and methods: We leverage a FL healthcare collaborative including data from 5 international healthcare systems (US and Europe) encompassing 42 hospitals. We implemented a COVID-19 computer vision diagnosis system using the FedAvg algorithm implemented on Clara Train SDK 4.0. To study the effect of data heterogeneity, training data was pooled from 3 systems locally and federation was simulated. We compared a centralized/pooled model, versus FedAvg, and 3 personalized FL variations (FedProx, FedBN, FedAMP).
Results: We observed comparable model performance with respect to internal validation (local model: AUROC 0.94 vs FedAvg: 0.95, p = 0.5) and improved model generalizability with the FedAvg model (p < 0.05). When investigating the effects of model heterogeneity, we observed poor performance with FedAvg on internal validation as compared to personalized FL algorithms. FedAvg did have improved generalizability compared to personalized FL algorithms. On average, FedBN had the best rank performance on internal and external validation.
Conclusion: FedAvg can significantly improve the generalization of the model compared to other personalization FL algorithms; however, at the cost of poor internal validity. Personalized FL may offer an opportunity to develop both internal and externally validated algorithms.