2023-05-10 タフツ大学
◆その結果、拡大した反復配列の近くでDNA切断が起こると、重要な遺伝子の欠失や癌などの疾病につながる可能性があることを発見した。研究チームは、DNAリピートの病気や癌の患者さんにおいて、DNAの修復や複製を促進するための標的となりうる2つのタンパク質を特定しました。
<関連情報>
- https://now.tufts.edu/2023/05/10/how-dna-repair-can-go-wrong-and-lead-disease
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-023-37901-2
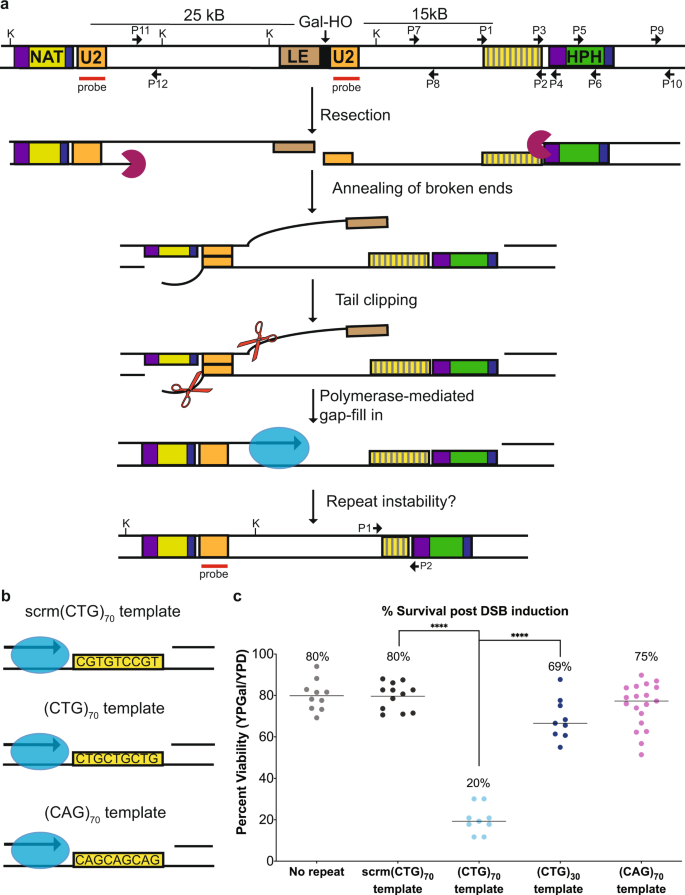
構造を形成するCAG/CTGリピートがギャップ修復を妨害し、リピート拡大や染色体切断を引き起こす Structure-forming CAG/CTG repeats interfere with gap repair to cause repeat expansions and chromosome breaks
Erica J. Polleys,Isabella Del Priore,James E. Haber & Catherine H. Freudenreich
Nature Communications Published:29 April 2023
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-023-37901-2
Abstract
Expanded CAG/CTG repeats are sites of DNA damage, leading to repeat length changes. Homologous recombination (HR) is one cause of repeat instability and we hypothesized that gap filling was a driver of repeat instability during HR. To test this, we developed an assay such that resection and ssDNA gap fill-in would occur across a (CAG)70 or (CTG)70 repeat tract. When the ssDNA template was a CTG sequence, there were increased repeat contractions and a fragile site was created leading to large-scale deletions. When the CTG sequence was on the resected strand, resection was inhibited, resulting in repeat expansions. Increased nucleolytic processing by deletion of Rad9, the ortholog of 53BP1, rescued repeat instability and chromosome breakage. Loss of Rad51 increased contractions implicating a protective role for Rad51 on ssDNA. Together, our work implicates structure-forming repeats as an impediment to resection and gap-filling which can lead to mutations and large-scale deletions.