2023-06-13 カリフォルニア大学リバーサイド校(UCR)
◆中国の病院から得られた実際のデータを使用した研究では、年齢や体重、追加の病気などの個々の特徴が、再発率を最も効果的に減少させる薬物の組み合わせを決定することが示されました。この研究は、個々の患者に合わせた医療の時代を迎える可能性があるとされています。
<関連情報>
- https://news.ucr.edu/articles/2023/06/13/best-drug-combos-prevent-covid-recurrence
- https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/frai.2023.1123285/full
COVID-19のコンビナトリアル治療選択について、実世界のデータから学ぶ
Learning from real world data about combinatorial treatment selection for COVID-19
Song Zhai, Zhiwei Zhang, Jiayu Liao and Xinping Cui
Frontiers in Artificial Intelligence Published:03 April 2023
DOI:https://doi.org/10.3389/frai.2023.1123285
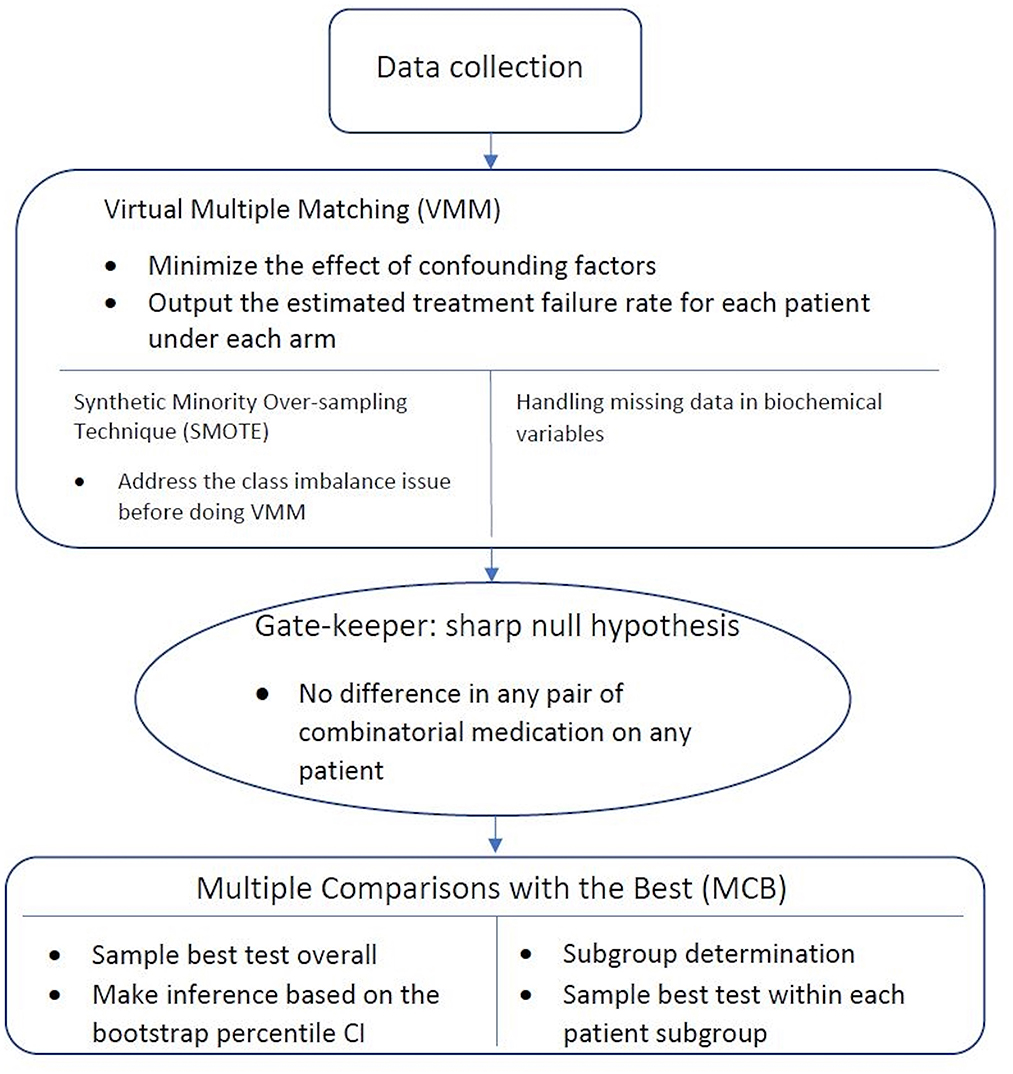
COVID-19 is an unprecedented global pandemic with a serious negative impact on virtually every part of the world. Although much progress has been made in preventing and treating the disease, much remains to be learned about how best to treat the disease while considering patient and disease characteristics. This paper reports a case study of combinatorial treatment selection for COVID-19 based on real-world data from a large hospital in Southern China. In this observational study, 417 confirmed COVID-19 patients were treated with various combinations of drugs and followed for four weeks after discharge (or until death). Treatment failure is defined as death during hospitalization or recurrence of COVID-19 within four weeks of discharge. Using a virtual multiple matching method to adjust for confounding, we estimate and compare the failure rates of different combinatorial treatments, both in the whole study population and in subpopulations defined by baseline characteristics. Our analysis reveals that treatment effects are substantial and heterogeneous, and that the optimal combinatorial treatment may depend on baseline age, systolic blood pressure, and c-reactive protein level. Using these three variables to stratify the study population leads to a stratified treatment strategy that involves several different combinations of drugs (for patients in different strata). Our findings are exploratory and require further validation.