2024-12-04 カロリンスカ研究所(KI)
<関連情報>
- https://news.ki.se/long-term-benefit-from-anti-hormonal-treatment-is-influenced-by-menopausal-status
- https://academic.oup.com/jnci/advance-article/doi/10.1093/jnci/djae268/7915220
乳癌患者における閉経状態による長期タモキシフェン療法の有益性の違い:対照ランダム化臨床試験の二次解析 Differential long-term tamoxifen therapy benefit by menopausal status in breast cancer patients: secondary analysis of a controlled randomized clinical trial
Annelie Johansson, MSc, PhD, Huma Dar, MSc, PhD, Anna Nordenskjöld, MD, PhD, Gizeh Perez-Tenorio, MSc, PhD, Nicholas P Tobin, MSc, PhD, Christina Yau, PhD, Christopher C Benz, MD, Laura J Esserman, MD, Laura J van ‘t Veer, MSc, PhD, Bo Nordenskjöld, MD, PhD …
Journal of the National Cancer Institute Published:04 December 2024
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1093/jnci/djae268
Abstract
Background
Estrogen receptor–positive breast cancer patients have a long-term risk of distant metastatic disease, and premenopausal patients have a higher risk. Randomized studies with long-term follow-up are essential to understand treatment benefit. We elucidated the long-term tamoxifen therapy benefit by menopausal status in the Stockholm tamoxifen trials with 20 years complete follow-up.
Methods
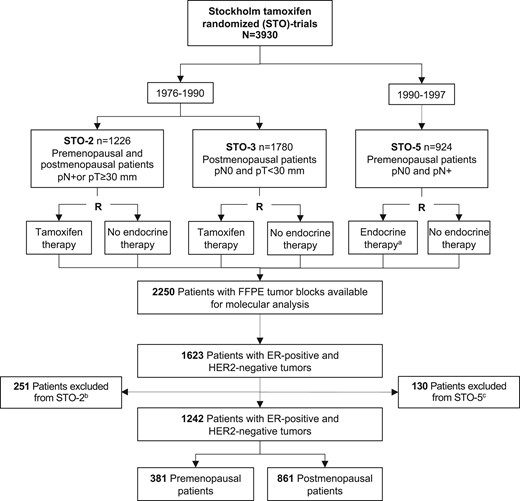
Secondary analysis of 1242 estrogen receptor–positive and HER2-negative patients that were randomly assigned to 2-5 years of 40 mg adjuvant tamoxifen or no endocrine therapy. Distant recurrence-free interval in tamoxifen-treated vs endocrine untreated patients was assessed by Kaplan–Meier, Cox proportional hazards regression, and time-varying analyses.
Results
In premenopausal patients, a statistically significant tamoxifen benefit was observed for lymph node–negative (adjusted hazard ratio [HR] = 0.46, 95% confidence interval [CI] = 0.24 to 0.87), progesterone receptor–positive (adjusted HR = 0.61, 95% CI = 0.41 to 0.91), and genomic low-risk tumors (adjusted HR = 0.47, 95% CI = 0.26 to 0.85) but only lasted beyond 10 years for genomic low-risk tumors. Postmenopausal patients showed long-term benefit for all good-prognosis markers including low-grade (adjusted HR = 0.55, 95% CI = 0.41 to 0.73), lymph node–negative (adjusted HR = 0.44, 95% CI = 0.30 to 0.64), progesterone receptor–positive (adjusted HR = 0.60, 95% CI = 0.44 to 0.80), Ki-67 low (adjusted HR = 0.51, 95% CI = 0.38 to 0.68), and genomic low-risk tumors (adjusted HR = 0.53, 95% CI = 0.37 to 0.74), and regardless of tumor size (≤20 mm: adjusted HR = 0.55, 95% CI = 0.39 to 0.77; >20 mm: adjusted HR = 0.64, 95% CI = 0.44 to 0.94). Premenopausal patients with no poor-prognosis tumor characteristics (clinical marker score = 0) showed early benefit and postmenopausal long-term benefit.
Conclusions
Our study suggests differential tamoxifen benefit by menopausal status. Improved long-term endocrine therapy prediction in premenopausal patients is needed and could involve molecular markers because standard tumor characteristics cannot predict benefit beyond 10 years.