2025-04-25 東京大学
<関連情報>
- https://www.h.u-tokyo.ac.jp/press/20250424-2.html
- https://www.h.u-tokyo.ac.jp/press/__icsFiles/afieldfile/2025/04/24/release_20250424-2.pdf
- https://www.internationaljournalofcardiology.com/article/S0167-5273(25)00246-3/fulltext
自宅での単一誘導心電図による心不全モニタリング Heart failure monitoring with a single‑lead electrocardiogram at home
Eriko Hasumi ∙ Katsuhito Fujiu ∙ Ying Chen ∙ … ∙ Hiroshi Akazawa ∙ Morio Shoda ∙ Issei Komuro
International Journal of Cardiology Published: April 24, 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijcard.2025.133203
Highlights
- We developed an AI-based HF detection system using single‑lead ECGs recorded at home.
- Our CNN model calculated an HF-index from the estimated NYHA grades as an indicator of HF severity.
- We constructed an at-home HF monitoring system enabling early detection and treatment in HF.
- AI analyzes ECGs from portable devices to detect HF early, enabling swift medical attendance.
Abstract
Background
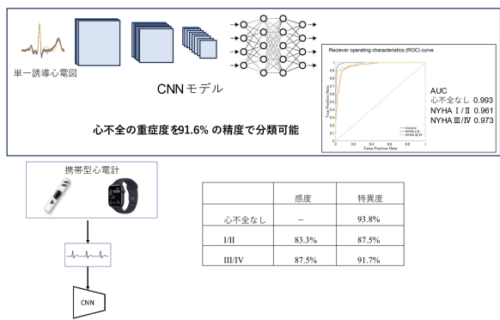
Repeated hospitalization due to heart failure (HF) is a significant predictor of mortality. However, there are limited early detection systems for HF progression that can be utilized by patients at home without a cardiac implantable electrical device (CIED). This study aimed to develop an artificial intelligence (AI)-based system utilizing convolutional neural network (CNN) algorithms for the early detection of HF progression using single‑lead electrocardiograms (ECGs), including those obtained from wearable devices such as the Apple Watch®.
Methods
ECG data from 9518 participants, encompassing both HF patients and healthy controls, were used to train the CNN model to diagnose HF status. New York Heart Association (NYHA) classifications were determined by multiple cardiologists at the time of ECG recording. The CNN model was designed to calculate a novel HF-index, derived from the NYHA grades predicted by the AI, as a quantitative measure of real-time HF severity.
Results
The CNN model achieved a 91.6 % accuracy in classifying HF severity into NYHA I–II (asymptomatic to mild HF) and NYHA III–IV grades (moderate to severe HF) categories. Furthermore, the model generated a novel HF-index as a real-time indicator of HF severity, which showed a positive correlation (R = 0.74) with plasma B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP) levels, thereby validating its effectiveness in reflecting HF severity.
Conclusions
We successfully constructed a novel at-home HF monitoring system utilizing a portable single‑lead ECG device. This system has been validated for its effectiveness in at-home HF monitoring, representing a significant advancement in remote healthcare for HF management.