2025-04-25 京都大学
<関連情報>
- https://www.kyoto-u.ac.jp/ja/research-news/2025-04-25
- https://www.kyoto-u.ac.jp/sites/default/files/2025-04/web_2504_Furukawa-5a1728c7cd9583977f8f4748968d5075.pdf
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41591-025-03639-1
地域の成人の閾値未満うつ病に対するスマートフォンアプリを介した認知行動療法スキル:RESiLIENT無作為化比較試験 Cognitive behavioral therapy skills via a smartphone app for subthreshold depression among adults in the community: the RESiLIENT randomized controlled trial
Toshi A. Furukawa,Aran Tajika,Rie Toyomoto,Masatsugu Sakata,Yan Luo,Masaru Horikoshi,Tatsuo Akechi,Norito Kawakami,Takeo Nakayama,Naoki Kondo,Shingo Fukuma,Ronald C. Kessler,Helen Christensen,Alexis Whitton,Inbal Nahum-Shani,Wolfgang Lutz,Pim Cuijpers,James M. S. Wason & Hisashi Noma
Nature Medicine Published:23 April 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-025-03639-1
Abstract
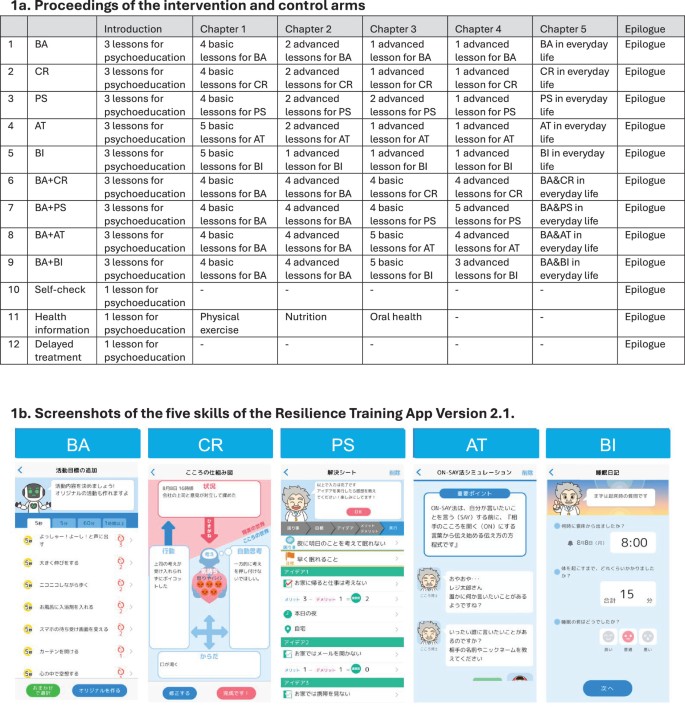
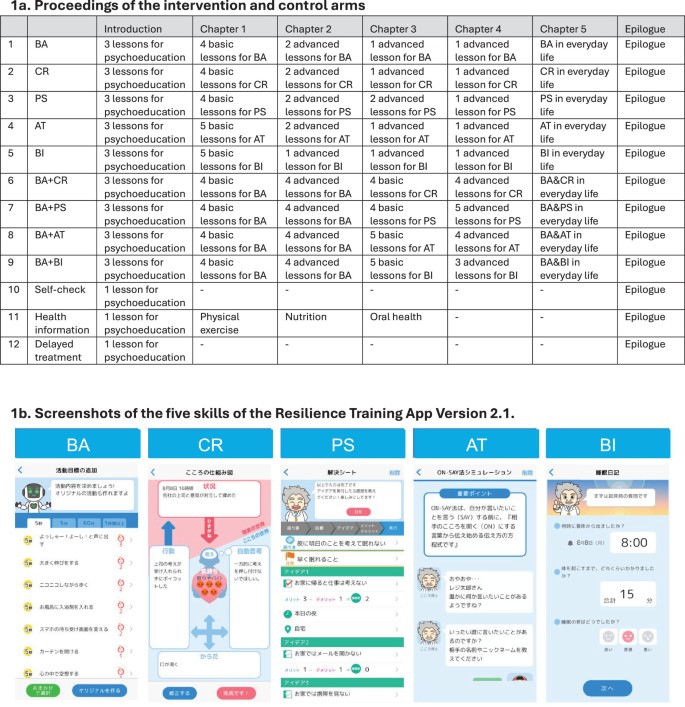
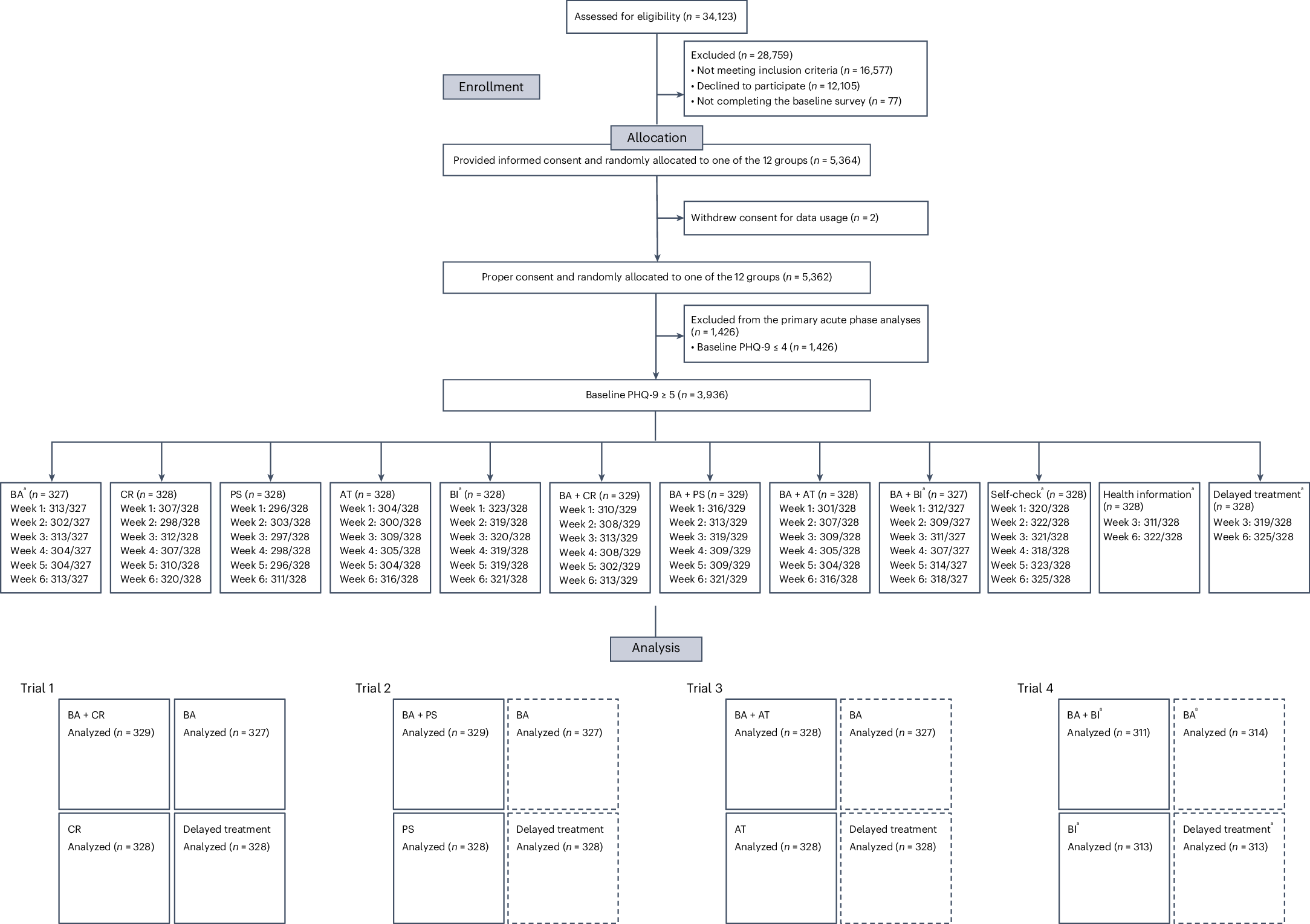
Subthreshold depression, defined as a depressive status falling short of the diagnostic threshold for major depression, is common, disabling and constitutes a risk factor for future depressive episodes. Cognitive behavioral therapies (CBT) have been shown to be effective but are usually provided as packages of various skills. Little research has been done to investigate whether all their components are beneficial and contributory to mental health promotion. We addressed this issue by developing a smartphone CBT app that implements five representative CBT skills (behavioral activation, cognitive restructuring, problem solving, assertion training and behavior therapy for insomnia), and conducting a master randomized study that included four 2 × 2 factorial trials to enable precise estimation of skill-specific efficacies. Between September 2022 and February 2024, we recruited 3,936 adult participants with subthreshold depression. Among those randomized, the follow-up rate was 97% at week 6 and adherence to the app was 84%. The study showed that all included CBT skills and their combinations differentially beat all three control conditions of delayed treatment, health information or self-check, with effect sizes ranging between -0.67 (95% confidence interval: -0.81 to -0.53) and -0.16 (-0.30 to -0.02) for changes in depressive symptom severity from baseline to week 6, as measured with the Patient Health Questionnaire-9 scores. Knowledge of the active ingredients of CBT can better inform the design of more effective and scalable psychotherapies in the future. (UMIN Clinical Trials Registry UMIN000047124).