2025-06-03 理化学研究所
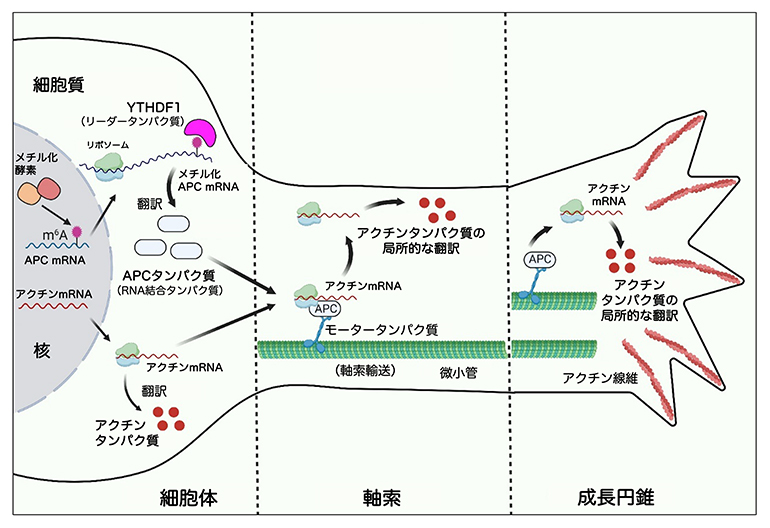
YTHDF1による細胞体でのAPC翻訳促進と、APCによる成長円錐でのアクチン翻訳促進
<関連情報>
- https://www.riken.jp/press/2025/20250603_3/index.html
- https://www.cell.com/cell-reports/fulltext/S2211-1247(25)00498-X
m6A RNAメチル化を介したグローバルAPC発現制御は、β-アクチンの局所翻訳と軸索の発達に必要であ m6A RNA methylation-mediated control of global APC expression is required for local translation of β-actin and axon development
Loic Broix ∙ Rohini Roy ∙ Belal Shohayeb ∙ Ikumi Oomoto ∙ Hiroki Umeshima ∙ Dan Ohtan Wang
Cell Reports Published:May 20, 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2025.115727
Highlights
•APC expression in the neuronal soma is m6A dependent
•The m6A machinery controls β-actin mRNA axonal transport and translation via APC expression
•m6A/YTHDFs/APC pathway is required for axon development
Summary
The spatial regulation of mRNAs in neurons, including their localization and translation, is controlled by RNA-binding proteins and is critical for neuronal development. In this study, we present evidence that the multifunctional RNA-binding protein adenomatous polyposis coli (APC) is encoded by an mRNA modified with N6-methyladenosine (m6A). This modification facilitates the translation of APC in neuronal somata via YTH domain-containing family (YTHDF) m6A reader proteins. Disrupted APC expression, caused by reduced expression of the m6A writer METTL14 or reader YTHDF1, or by overexpression of METTL14 mutants carrying human missense mutations linked to autism and schizophrenia, impairs the transport and local translation of APC-regulated target mRNA β-actin in axons and growth cones. Such disruptions consequently hinder axon development both in vitro and in vivo. These findings reveal a mechanism by which m6A-regulated global expression of the RNA-binding protein APC governs axonal mRNA translation and development.