2025-06-12 東京科学
<関連情報>
- https://www.isct.ac.jp/ja/news/ti4ztndoad8r
- https://www.isct.ac.jp/plugins/cms/component_download_file.php?type=2&pageId=&contentsId=1&contentsDataId=1732&prevId=&key=df83756d02e9ae2a5701f8f908b91917.pdf
- https://journals.asm.org/doi/10.1128/msystems.01575-24
漬物由来のLactiplantibacillus plantarumとLactiplantibacillus pentosusの免疫調節能に関する比較ゲノム解析 Comparative genome analysis of the immunomodulatory ability of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum and Lactiplantibacillus pentosus from Japanese pickles
Yiting Liu, Kazunori Sawada8, Takahiko Adachi, Yuta Kino, Tingyu Yin, Naoyuki Yamamoto, Takuji Yamada
mSystems Published:29 April 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1128/msystems.01575-24
ABSTRACT
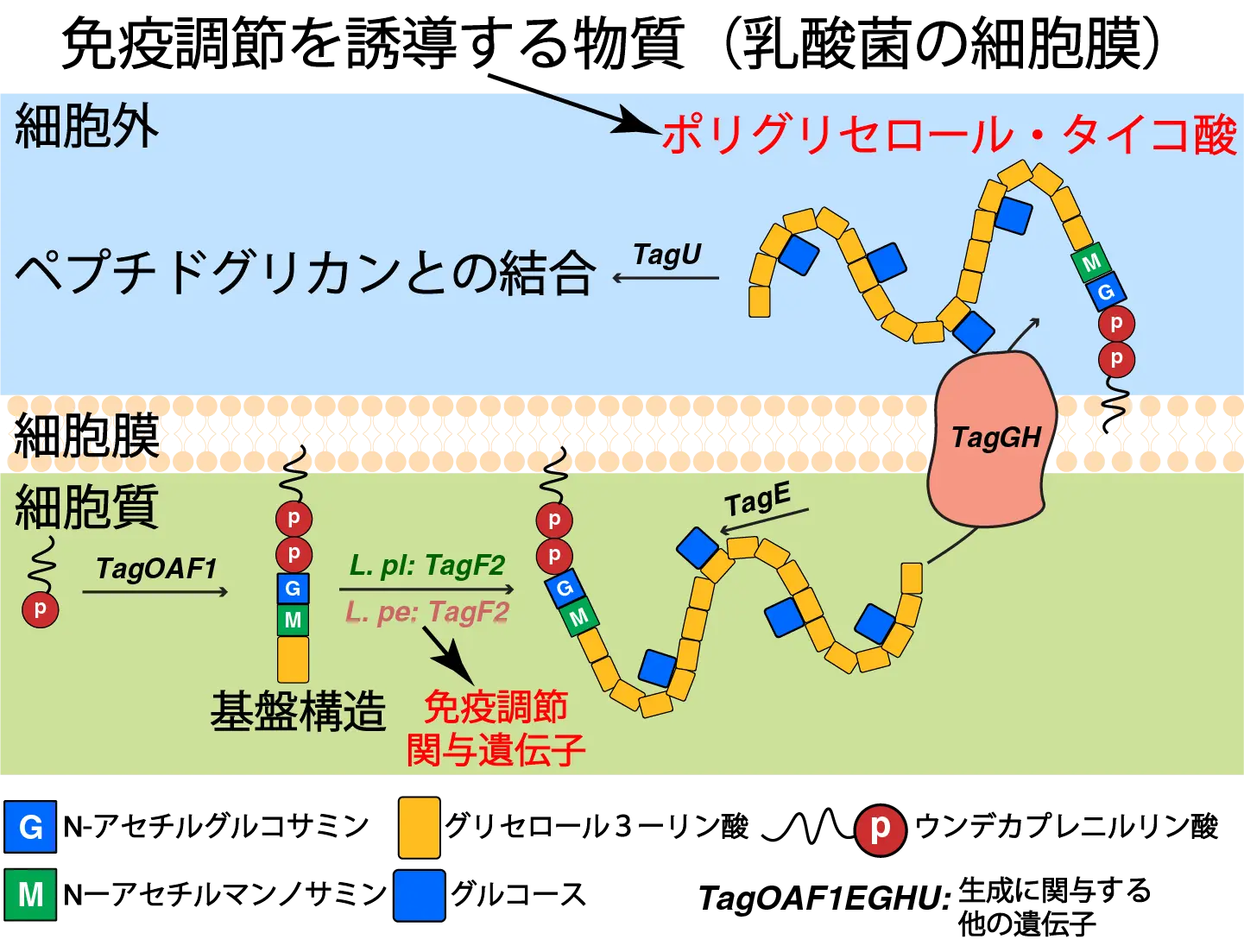
Lactic acid bacteria (LAB) are pivotal in food preservation and exhibit immunomodulatory effects on interleukin-10 (IL-10) and interleukin-12 (IL-12) production. Lactiplantibacillus plantarum (L. plantarum) and Lactiplantibacillus pentosus (L. pentosus) from fermented food are known for their effect; however, a comprehensive comparative genome analysis is needed to identify the linked genes. Here, we investigated the immunomodulatory capability at the genome level of L. plantarum and L. pentosus strains isolated from Japanese pickles at the genome level, and we further identified their immunomodulation-associated genes using the potential-gene (PG) index derived from the Calinski–Harabasz (CH) index. The results revealed an immunostimulatory clade with strain-specific IL-10 and IL-12 induction and identified key genes via the PG index. Both genes across two species were shown to encode the enzyme TagF2, which is crucial for synthesizing poly-glycerol-3-phosphate type wall teichoic acid (poly-GroP WTA), indicating that TagF2 plays a potential role as an effective microbe-associated-molecular-pattern. In vivo analyses confirmed the IL-10-inducing ability of one strain, reinforcing the IL-10-stimulating capacity of its poly-GroP WTA. Subpotential genes in L. plantarum TagF2-possessing strains were linked to host‒cell interactions, suggesting that such strains play potential probiotic roles. Collectively, the PG index effectively identified immunomodulation-related genes, thus paving the way for the use of the PG index to detect potential health benefit-associated genes in other LAB species.