2025-10-31 京都大学
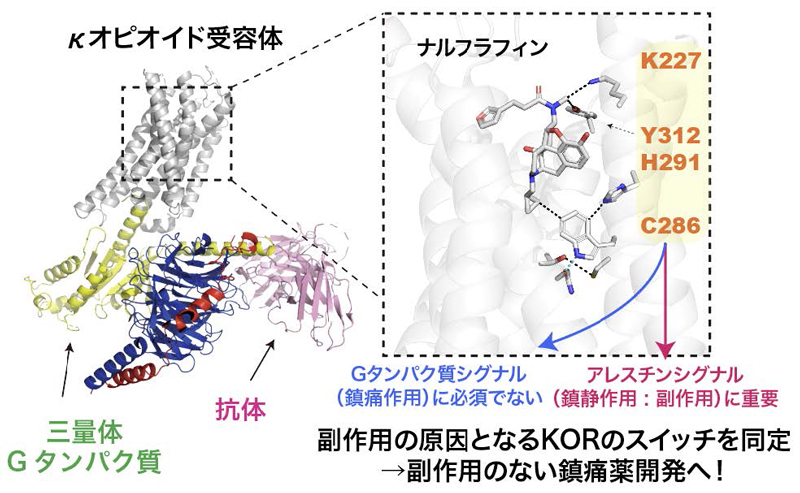
本研究の概要図
<関連情報>
- https://www.kyoto-u.ac.jp/ja/research-news/2025-10-31
- https://www.kyoto-u.ac.jp/sites/default/files/2025-10/web_2510_Inoue-4a614821bbbe6d613b16872c0fbe69dc.pdf
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-025-64882-1
ヒトκオピオイド受容体のバイアスシグナル伝達機構に関する構造的および動的知見 Structural and dynamic insights into the biased signaling mechanism of the human kappa opioid receptor
Chiyo Suno-Ikeda,Ryo Nishikawa,Riko Suzuki,Shun Yokoi,Seiya Iwata,Tomoyo Takai,Takaya Ogura,Mika Hirose,Akihisa Tokuda,Risako Katamoto,Akitoshi Inoue,Eri Asai,Ryoji Kise,Yukihiko Sugita,Takayuki Kato,Hiroshi Nagase,Ayori Mitsutake,Tsuyoshi Saitoh,Kota Katayama,Asuka Inoue,Hideki Kandori,Takuya Kobayashi & Ryoji Suno
Nature Communications Published:28 October 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-025-64882-1
Abstract
The κ-opioid receptor (KOR) is a member of the G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) family, modulating cellular responses through transducers such as G proteins and β-arrestins. G-protein-biased KOR agonists aim to retain analgesic and antipruritic actions while limiting aversion and sedation. Aiming to inform G-biased KOR agonist design, we analyze signaling-relevant residues from structural and dynamic views. Here we show, using multiple complementary methods, shared residues that determine β-arrestin recruitment by nalfurafine and U-50,488H. Cryo-electron microscopy structures of the KOR-Gi signaling complexes identify the ligand binding mode in the activated state. Vibrational spectroscopy reveals ligand-induced conformational changes. Cell-based mutant experiments pinpoint four amino acids (K2275.40, C2866.47, H2916.52, and Y3127.34; Ballesteros–Weinstein numbering is shown in superscript) that play crucial roles in β-arrestin recruitment. Furthermore, MD simulations revealed that the four mutants tend to adopt conformations with reduced β-arrestin recruitment activity. Our research findings provide a foundation for enhancing KOR-mediated therapeutic effects while minimizing unwanted side effects by targeting specific residues within the KOR ligand-binding pocket, including K2275.40 and Y3127.34, which have previously been implicated in biased signaling.


