急性骨髄性白血病との闘いに人工知能が役立つ Artificial intelligence aids fight against acute myeloid leukemia
2023-11-14 デラウェア大学 (UD)
◆AMLは血液がんで、患者の独自の遺伝的プロファイルに基づいた個別化された治療への一歩であり、効果が高く副作用が少ない治療を可能にします。
◆彼は遺伝データを使用し、機械学習を活用してAML患者が異なる薬物療法に対する「高反応者」または「低反応者」であるかを判断しました。この研究は将来の患者に対する有望な結果の基盤を築くものであり、他のがんデータセットや薬物療法に対する戦略の影響を検討することも期待されています。
<関連情報>
- https://www.udel.edu/udaily/2023/november/mauricio-ferrato-sunita-chandrasekaran-erin-crowgey-artificial-intelligence-acute-myeloid-leukemia/
- https://academic.oup.com/bioinformaticsadvances/article/3/1/vbad034/7083432?login=false
RTK-Ⅲ阻害薬に対する反応を予測する機械学習分類法、トランスクリプトームシグネチャーとex vivoデータを用いて高い精度を示す Machine learning classifier approaches for predicting response to RTK-type-III inhibitors demonstrate high accuracy using transcriptomic signatures and ex vivo data
Mauricio H Ferrato, Adam G Marsh, Karl R Franke, Benjamin J Huang, E Anders Kolb, Deborah DeRyckere, Douglas K Grahm, Sunita Chandrasekaran, Erin L Crowgey
Bioinformatics Advances Published:22 March 2023
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1093/bioadv/vbad034
Abstract
Motivation
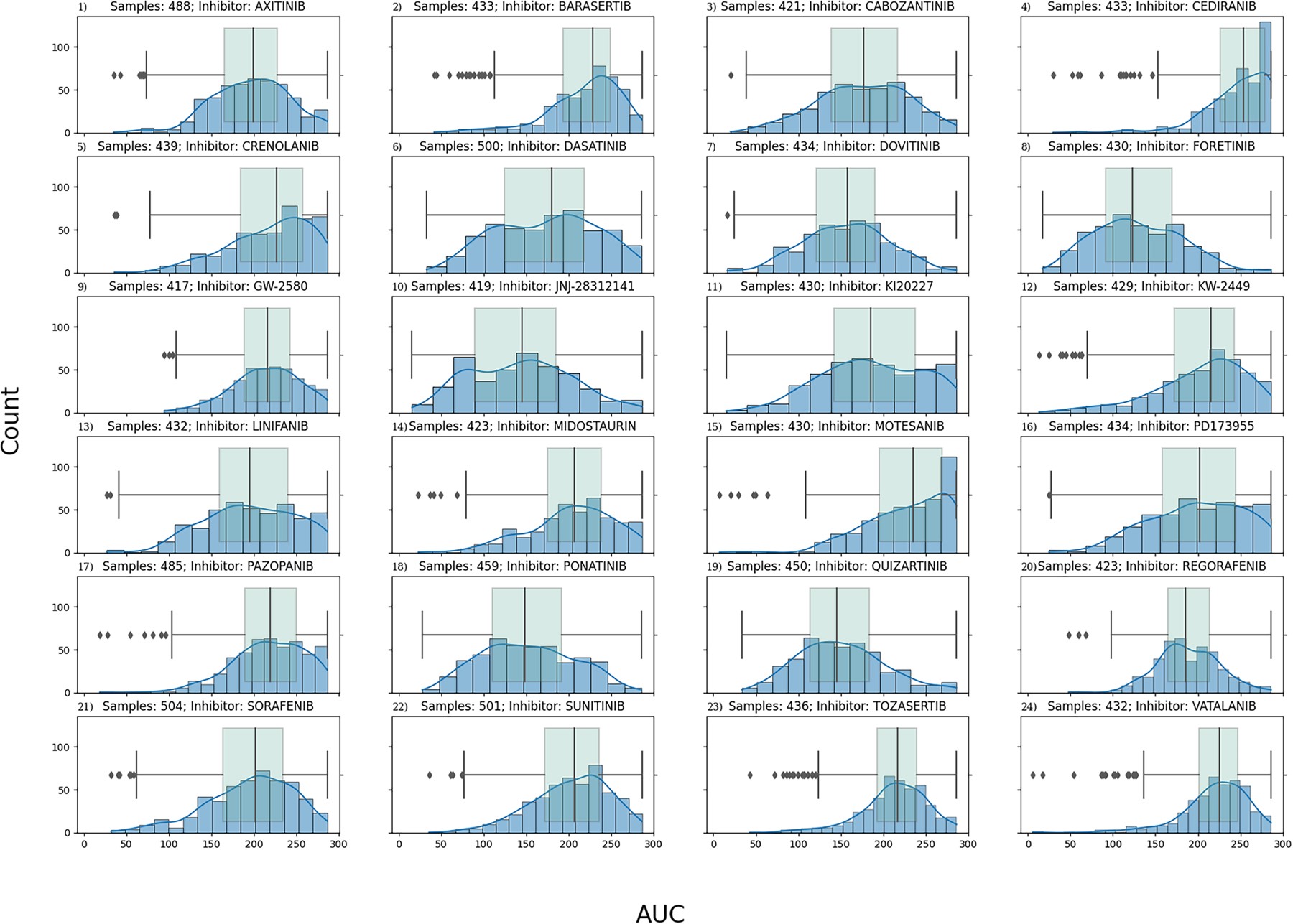
The application of machine learning (ML) techniques in the medical field has demonstrated both successes and challenges in the precision medicine era. The ability to accurately classify a subject as a potential responder versus a nonresponder to a given therapy is still an active area of research pushing the field to create new approaches for applying machine-learning techniques. In this study, we leveraged publicly available data through the BeatAML initiative. Specifically, we used gene count data, generated via RNA-seq, from 451 individuals matched with ex vivo data generated from treatment with RTK-type-III inhibitors. Three feature selection techniques were tested, principal component analysis, Shapley Additive Explanation (SHAP) technique and differential gene expression analysis, with three different classifiers, XGBoost, LightGBM and random forest (RF). Sensitivity versus specificity was analyzed using the area under the curve (AUC)-receiver operating curves (ROCs) for every model developed.
Results
Our work demonstrated that feature selection technique, rather than the classifier, had the greatest impact on model performance. The SHAP technique outperformed the other feature selection techniques and was able to with high accuracy predict outcome response, with the highest performing model: Foretinib with 89% AUC using the SHAP technique and RF classifier. Our ML pipelines demonstrate that at the time of diagnosis, a transcriptomics signature exists that can potentially predict response to treatment, demonstrating the potential of using ML applications in precision medicine efforts.
Availability and implementation
https://github.com/UD-CRPL/RCDML.
Supplementary information
Supplementary data are available at Bioinformatics Advances online.