2022-03-22 南洋(ナンヤン)理工大学(NTU)
・NTUと早稲田大学の研究者らは、2月に学術誌「Metabolites」で発表した実験により、発酵させたおからを加えた高脂肪食を与えたマウスは、同じ食事を与えたが発酵させたおからを与えていないマウスに比べて、3週間後の体重増加が少なく、脂肪とコレステロールのレベルも低くなっていることを示しました。
<関連情報>
- https://www.ntu.edu.sg/news/detail/fighting-obesity-with-fermented-soybean-waste
- https://www.mdpi.com/2218-1989/12/3/198
Aspergillus属菌による固体発酵おからが脂質代謝を改善し、高脂肪食誘発性肥満が改善される Solid-State Fermented Okara with Aspergillus spp. Improves Lipid Metabolism and High-Fat Diet Induced Obesity
Natsumi Ichikawa 1 , Li Shiuan Ng 2 , Saneyuki Makino 1 , Luo Lin Goh 2 , Yun Jia Lim 2 , Ferdinandus 2 , Hiroyuki Sasaki 1 , Shigenobu Shibata 1,* and Chi-Lik Ken Lee 2,*
1 Laboratory of Physiology and Pharmacology, School of Advanced Science and Engineering, Waseda University, Wakamatsu-cho 2-2, Shinjuku-ku, Tokyo 162-8480, Japan; natsu3@ruri.waseda.jp (N.I.); s.makino@fuji.waseda.jp (S.M.); hiroyuki-sasaki@asagi.waseda.jp (H.S.)
2 Division of Chemistry and Biological Chemistry, School of Physical and Mathematical Sciences, Nanyang Technological University, 21 Nanyang Link, Singapore 637371, Singapore; lishiuan001@e.ntu.edu.sg (L.S.N.); gohl0023@e.ntu.edu.sg (L.L.G.); limy0263@e.ntu.edu.sg (Y.J.L.); fe0003us@e.ntu.edu.sg (F.)
3 Correspondence: shibatas@waseda.jp (S.S.); ken.lee@ntu.edu.sg (C.-L.K.L.); Tel.: +81-3-5369-7318 (S.S.); +65-6513-2178 (C.-L.K.L.)
Abstract
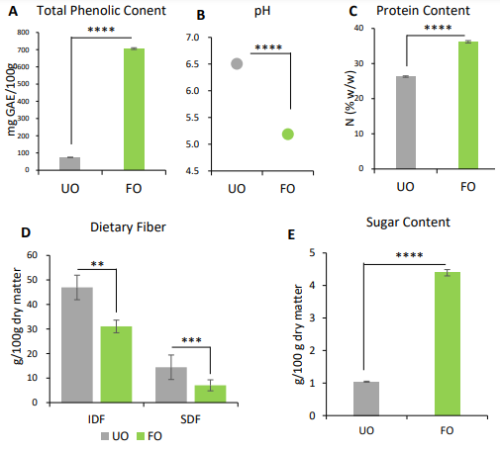
Okara is a major by-product of soymilk and tofu production. Despite retaining abundant nutrients after the process, okara is often under-utilized. In this study, solid-state fermentation (SSF) of okara was carried out using a koji starter (containing both Aspergillus oryzae and Aspergillus sojae) with the intention of releasing its untapped nutrients. Its effects on lipid metabolism in diet-induced obesity (DIO) were observed. The nutritional profile of fermented okara was elucidated using the following parameters: total phenolic content (TPC), pH, protein content, dietary fiber, amino acid content, and free sugar content. In vivo experiments were conducted using high-fat diets supplemented with unfermented okara and fermented okara over three weeks. Supplementation with fermented okara reduced body weight gain, adipose tissue weight, the serum triglyceride profile, and lipid accumulation in the liver, and altered the mRNA expression levels related to lipid metabolism; however, it did not affect pH and short-chain fatty acid (SCFA) production in this study. In conclusion, high-fat diets supplemented using okara fermented with Aspergillus spp. improved the lipid metabolism in mice, due to their high nutritional value, such as TPC, soy protein, and amino acids, and their synergistic effects without altering the gut microbiota. Keywords: okara; Aspergillus oryzae; Aspergillus sojae; solid-state fermentation; anti-obesity