細胞骨格を構成する微小管の構成要素であるチューブリン。新しい方法により、癌を含む疾患におけるその役割の詳細な研究が可能になった。 Tubulins are the building blocks of microtubules, which make up the cell’s skeleton. A new method enables the detailed study of their role in diseases, including cancer.
◆特に、α-チューブリンのテール部分の修飾は重要であり、ポリグルタミン化とデチロシネーションという修飾が安定なマイクロチューブに存在します。これらの修飾の組み合わせを「チューブリンコード」と呼び、マイクロチューブの特定の機能と関連付けられます。チューブリンの修飾の異常はがんや神経変性疾患などの病気と関連しており、修飾の重要性を理解することは病気の知識の進歩や治療法の開発に重要です。しかし、チューブリン修飾の機能と調節のメカニズムはまだよく理解されておらず、研究にはさまざまな困難があります。
◆最近の研究では、チューブリン修飾を持つ完全に機能的なチューブリンを設計するための化学的手法が開発され、修飾の特定の組み合わせによるマイクロチューブの機能の調節の仕組みが解明されました。この研究は、チューブリンの分子機能の理解と修飾の異常が病気にどのように関連しているかについての洞察を提供するとともに、新たな研究手法を示しています。
<関連情報>
- https://actu.epfl.ch/news/cracking-the-tubulin-code/
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41557-023-01228-8
半合成によるチューブリン工学で、ポリグルタミル化がデチロシン化を誘導することが明らかになった Tubulin engineering by semi-synthesis reveals that polyglutamylation directs detyrosination
Eduard Ebberink,Simon Fernandes,Georgios Hatzopoulos,Ninad Agashe,Po-Han Chang,Nora Guidotti,Timothy M. Reichart,Luc Reymond,Marie-Claire Velluz,Fabian Schneider,Cédric Pourroy,Carsten Janke,Pierre Gönczy,Beat Fierz & Charlotte Aumeier
Nature Chemistry Published:29 June 2023
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41557-023-01228-8
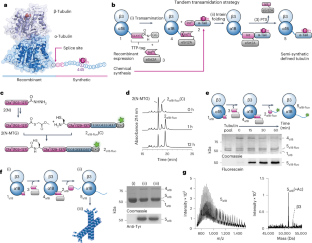
Abstract
Microtubules, a critical component of the cytoskeleton, carry post-translational modifications (PTMs) that are important for the regulation of key cellular processes. Long-lived microtubules, in neurons particularly, exhibit both detyrosination of α-tubulin and polyglutamylation. Dysregulation of these PTMs can result in developmental defects and neurodegeneration. Owing to a lack of tools to study the regulation and function of these PTMs, the mechanisms that govern such PTM patterns are not well understood. Here we produce fully functional tubulin carrying precisely defined PTMs within its C-terminal tail. We ligate synthetic α-tubulin tails—which are site-specifically glutamylated—to recombinant human tubulin heterodimers by applying a sortase- and intein-mediated tandem transamidation strategy. Using microtubules reconstituted with these designer tubulins, we find that α-tubulin polyglutamylation promotes its detyrosination by enhancing the activity of the tubulin tyrosine carboxypeptidase vasohibin/small vasohibin-binding protein in a manner dependent on the length of polyglutamyl chains. We also find that modulating polyglutamylation levels in cells results in corresponding changes in detyrosination, corroborating the link between the detyrosination cycle to polyglutamylation.