2025-08-04 マウントサイナイ医療システム(MSHS)
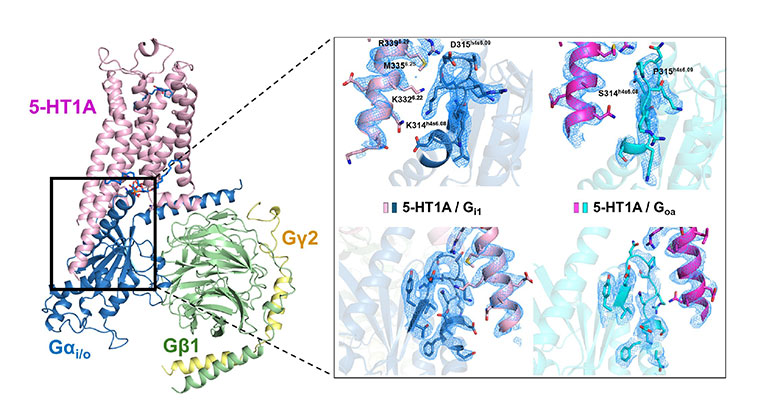
High-resolution 3D image showing how the 5-HT1A receptor connects with internal signaling proteins (G proteins). The highlighted areas reveal key contact points between the receptor and two different types of G proteins, captured using advanced cryo-electron microscopy. From A.L Warren et al., Structural determinants of G protein subtype selectivity at the serotonin receptor 5-HT1A. Science Advances. 2025. This work is licensed under CC BY-NC 4.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/).
<関連情報>
- https://www.mountsinai.org/about/newsroom/2025/new-insights-about-brain-receptor-may-pave-way-for-nextgen-mental-health-drugs
- https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/sciadv.adu9851
セロトニン受容体5-HT1AにおけるGタンパク質サブタイプ選択性の構造的決定要因 Structural determinants of G protein subtype selectivity at the serotonin receptor 5-HT1A
Audrey L. Warren, Gregory Zilberg, Anwar Abbassi, Alejandro Abraham, […] , and Daniel Wacker
Science Advances Published:1 Aug 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.adu9851
Abstract
Activation of the serotonin receptor 5-HT1A has been shown to regulate mood and cognition, making 5-HT1A an important target in the treatment of anxiety, depression, and psychosis. Although the receptor signals through inhibitory G proteins, more work is necessary to understand differences in transducer coupling and its relation to functional activity. To develop a molecular understanding of the differences underlying transducer coupling and activation, we performed structure-activity relationship studies of 5-HT1A with distinct G proteins. Through a combination of in vitro assays, we identified a potent partial agonist that selectively engages a G protein subtype. We further investigated the differences in G protein engagement at 5-HT1A with cryo–electron microscopy, determining structures of 5-HT1A bound to distinct ligands and G protein subtypes. Combined with subsequent structure-guided mutagenesis and signaling assays, our studies uncover both orthosteric and allosteric determinants of agonist-specific stimulation of distinct transducers.